Structural mechanism of ligand activation in human calcium-sensing receptor
- PMID: 27434672
- PMCID: PMC4977154
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.13662
Structural mechanism of ligand activation in human calcium-sensing receptor
Abstract
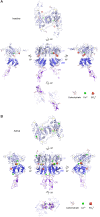
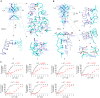
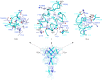
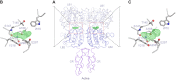
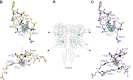
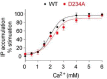
Human calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) is a G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that maintains extracellular Ca(2+) homeostasis through the regulation of parathyroid hormone secretion. It functions as a disulfide-tethered homodimer composed of three main domains, the Venus Flytrap module, cysteine-rich domain, and seven-helix transmembrane region. Here, we present the crystal structures of the entire extracellular domain of CaSR in the resting and active conformations. We provide direct evidence that L-amino acids are agonists of the receptor. In the active structure, L-Trp occupies the orthosteric agonist-binding site at the interdomain cleft and is primarily responsible for inducing extracellular domain closure to initiate receptor activation. Our structures reveal multiple binding sites for Ca(2+) and PO4(3-) ions. Both ions are crucial for structural integrity of the receptor. While Ca(2+) ions stabilize the active state, PO4(3-) ions reinforce the inactive conformation. The activation mechanism of CaSR involves the formation of a novel dimer interface between subunits.
Keywords: amino acids; biochemistry; biophysics; calcium-sensing receptor; extracellular calcium homeostasis; extracellular domain structure; human; principal agonist; receptor activation mechanism; structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures












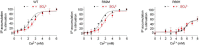


References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallographica Section D Biological Crystallography. 2010;66:213–221. doi: 10.1107/S0907444909052925. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai M, Quinn S, Trivedi S, Kifor O, Pearce SH, Pollak MR, Krapcho K, Hebert SC, Brown EM. Expression and characterization of inactivating and activating mutations in the human Ca2+o-sensing receptor. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271:19537–19545. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.32.19537. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

