ESOPEC: prospective randomized controlled multicenter phase III trial comparing perioperative chemotherapy (FLOT protocol) to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (CROSS protocol) in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (NCT02509286)
- PMID: 27435280
- PMCID: PMC4952147
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-016-2564-y
ESOPEC: prospective randomized controlled multicenter phase III trial comparing perioperative chemotherapy (FLOT protocol) to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (CROSS protocol) in patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (NCT02509286)
Abstract
Background: Recent randomized controlled trials comparing neoadjuvant chemoradiation plus surgery or perioperative chemotherapy plus surgery with surgery alone showed significant survival benefits for combined modality treatment of patients with localized esophageal adenocarcinoma. However, head-to-head comparisons of neoadjuvant chemoradiation and perioperative chemotherapy applying contemporary treatment protocols are lacking. The present trial was initiated to obtain valid information whether neoadjuvant chemoradiation or perioperative chemotherapy yields better survival in the treatment of localized esophageal adenocarcinoma.
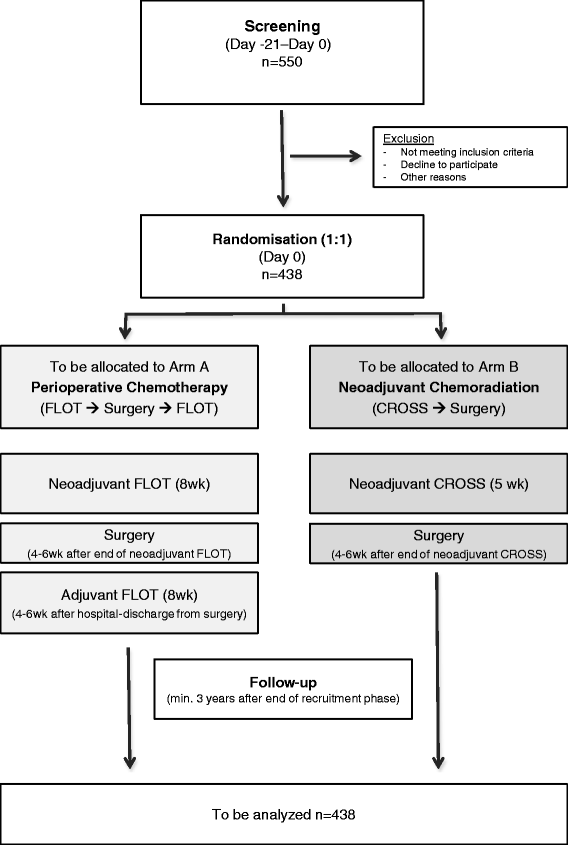
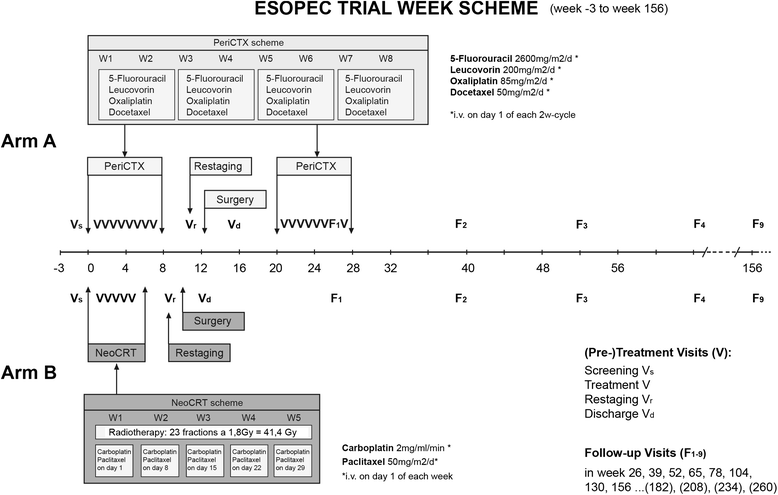
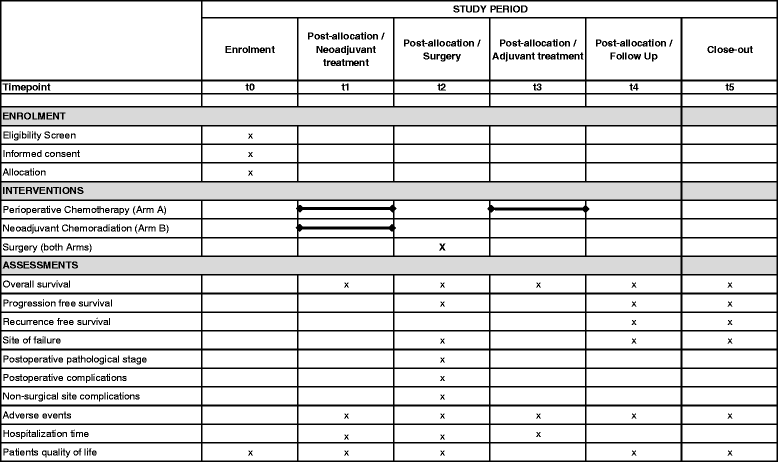
Methods/design: The ESOPEC trial is an investigator-initiated multicenter prospective randomized controlled two-arm trial, comparing the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemoradiation (CROSS protocol: 41.4Gy plus carboplatin/paclitaxel) followed by surgery versus perioperative chemotherapy and surgery (FLOT protocol: 5-FU/leucovorin/oxaliplatin/docetaxel) for the curative treatment of localized esophageal adenocarcinoma. Patients with cT1cN + cM0 and cT2-4acNxcM0 esophageal and junctional adenocarcinoma are eligible. The trial aims to include 438 participants who are centrally randomized to one of the two treatment groups in a 1:1 ratio stratified by N-stage and study site. The primary endpoint of the trial is overall survival assessed with a minimum follow-up of 36 months. Secondary objectives are progression-free survival, recurrence-free survival, site of failure, postoperative morbidity and mortality, duration of hospitalization as well as quality of life.
Discussion: The ESOPEC trial compares perioperative chemotherapy according to the FLOT protocol to neoadjuvant chemoradiation according to the CROSS protocol in multimodal treatment of non-metastasized recectable adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and the gastroesophageal junction. The goal of the trial is identify the superior protocol with regard to patient survival, treatment morbidity and quality of life.
Trial registration: NCT02509286 (July 22, 2015).
Keywords: Adenocarcinoma; Esophageal cancer; Neoadjuvant chemoradiation; Perioperative chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Moehler M, Baltin CT, Ebert M, et al. International comparison of the German evidence-based S3-guidelines on the diagnosis and multimodal treatment of early and locally advanced gastric cancer, including adenocarcinoma of the lower esophagus. Gastric Cancer. 2015;18(3):550–63. doi: 10.1007/s10120-014-0403-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical