In vivo and in vitro protective effects of omeprazole against neuropathic pain
- PMID: 27435304
- PMCID: PMC4951708
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30007
In vivo and in vitro protective effects of omeprazole against neuropathic pain
Abstract
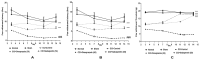
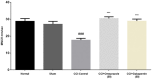
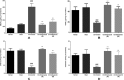
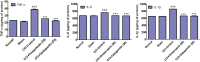
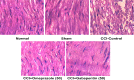
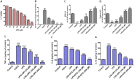
Apart from reducing the acid secretion, omeprazole inhibits activation of the nuclear factor-κB, release of inflammatory cytokines, and chemotaxis of neutrophils. These mechanisms prompted us to evaluate antineuropathic effect of omeprazole in the chronic constriction injury (CCI)-induced rat model of neuropathic pain and LPS mediated ROS-induced U-87 cells. Omeprazole at 50 mg/kg/day/oral for 14 days significantly reduced the intensity of neuropathic pain estimated as paw withdrawal latency, withdrawal pressure threshold and restored the motor nerve conduction velocity in the constricted nerve, when compared with respective groups. The histological findings revealed the protective effect of omeprazole against the CCI-induced damage. Omeprazole significantly decreased the levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) as compared to their respective control groups. It also reduced the oxidative stress by up regulating the SOD, catalase activity and decreasing MDA content. Similarly, in-vitro study, LPS mediated ROS-induced U-87 cells, omeprazole reduced the oxidative stress as well as the release of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6. Altogether, these results suggest that, neuroprotective effect of omeprazole is mediated through preventing release of proinflammatory cytokines, augmenting endogenous anti-oxidant defense system, and maintain the structural integrity of sciatic nerve from the CCI-induced structural damage and inflammatory changes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aloperine attenuated neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury via anti-oxidation activity and suppression of the nuclear factor kappa B pathway.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Sep 5;451(4):568-73. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.025. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25128276
-
Ligustrazine attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibition of JAK/STAT3 pathway in a rat model of chronic constriction injury.Pharmazie. 2016 Jul 7;71(7):408-412. doi: 10.1691/ph.2016.6546. Pharmazie. 2016. PMID: 29441918
-
The nitroxyl donor, Angeli's salt, reduces chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain.Chem Biol Interact. 2016 Aug 25;256:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.06.009. Epub 2016 Jun 7. Chem Biol Interact. 2016. PMID: 27287419 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary trypsin inhibitor attenuates the development of neuropathic pain following spinal nerve ligation.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Mar 17;590:150-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.01.070. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25643619
-
Montelukast attenuates neuropathic pain through inhibiting p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappa B in a rat model of chronic constriction injury.Anesth Analg. 2014 May;118(5):1090-6. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000174. Anesth Analg. 2014. PMID: 24686047
Cited by
-
Profiling and Identification of Omeprazole Metabolites in Mouse Brain and Plasma by Isotope Ratio-Monitoring Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometric Method.Life (Basel). 2020 Jul 19;10(7):115. doi: 10.3390/life10070115. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32707673 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Expression Alleviated Neuropathic Pain in a Chronic Constriction Nerve Injury Animal Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 24;23(19):11255. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911255. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36232555 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy on NOX5, mPGES1 and iNOS expression in Barrett's Esophagus.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 7;9(1):16242. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52800-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31700071 Free PMC article.
-
Ultra-diluted Toxicodendron pubescens attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokines and ROS- mediated neuropathic pain in rats.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 10;8(1):13562. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31971-9. Sci Rep. 2018. Retraction in: Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 11;9(1):8641. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44557-w. PMID: 30202036 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Pharmacological Effects and Toxicogenetic Impacts of Omeprazole: Genomic Instability and Cancer.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Mar 28;2020:3457890. doi: 10.1155/2020/3457890. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32308801 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kaur G. et al.. Anti-hyperalgesic and anti-nociceptive potentials of standardized grape seed proanthocyanidin extract against CCI-induced neuropathic pain in rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 27, 9–17 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Goecks C. S. et al.. Assessment of oxidative parameters in rat spinal cord after chronic constriction of the sciatic nerve. Neurochem.Res. 37, 1952–1958 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Pathak N. N. et al.. Antihyperalgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of atorvastatin in chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Inflam. 36, 1468–1478 (2013). - PubMed
-
- O’Connor A. B. & Dworkin R. H. Treatment of neuropathic pain: an overview of recent guidelines. Am. J. Med. 122, S22–S32 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

