Interaction of ARF-1.1 and neuronal calcium sensor-1 in the control of the temperature-dependency of locomotion in Caenorhabditis elegans
- PMID: 27435667
- PMCID: PMC4951722
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30023
Interaction of ARF-1.1 and neuronal calcium sensor-1 in the control of the temperature-dependency of locomotion in Caenorhabditis elegans
Abstract
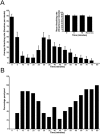
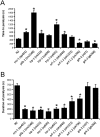
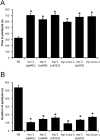
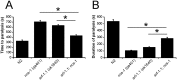
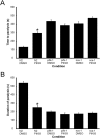
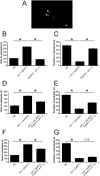
Neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1) mediates changes in cellular function by regulating various target proteins. Many potential targets have been identified but the physiological significance of only a few has been established. Upon temperature elevation, Caenorhabditis elegans exhibits reversible paralysis. In the absence of NCS-1, worms show delayed onset and a shorter duration of paralysis. This phenotype can be rescued by re-expression of ncs-1 in AIY neurons. Mutants with defects in four potential NCS-1 targets (arf-1.1, pifk-1, trp-1 and trp-2) showed qualitatively similar phenotypes to ncs-1 null worms, although the effect of pifk-1 mutation on time to paralysis was considerably delayed. Inhibition of pifk-1 also resulted in a locomotion phenotype. Analysis of double mutants showed no additive effects between mutations in ncs-1 and trp-1 or trp-2. In contrast, double mutants of arf-1.1 and ncs-1 had an intermediate phenotype, consistent with NCS-1 and ARF-1.1 acting in the same pathway. Over-expression of arf-1.1 in the AIY neurons was sufficient to rescue partially the phenotype of both the arf-1.1 and the ncs-1 null worms. These findings suggest that ARF-1.1 interacts with NCS-1 in AIY neurons and potentially pifk-1 in the Ca(2+) signaling pathway that leads to inhibited locomotion at an elevated temperature.
Figures
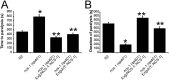
Similar articles
-
Identification of key structural elements for neuronal calcium sensor-1 function in the regulation of the temperature-dependency of locomotion in C. elegans.Mol Brain. 2013 Aug 27;6:39. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-6-39. Mol Brain. 2013. PMID: 23981466 Free PMC article.
-
KChIP-like auxiliary subunits of Kv4 channels regulate excitability of muscle cells and control male turning behavior during mating in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 4;35(5):1880-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3429-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25653349 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of neuronal calcium sensor-1 and ADP-ribosylation factor 1 allows bidirectional control of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase beta and trans-Golgi network-plasma membrane traffic.J Biol Chem. 2005 Feb 18;280(7):6047-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413090200. Epub 2004 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15576365
-
Cellular roles of neuronal calcium sensor-1 and calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinases in fungi.J Basic Microbiol. 2011 Apr;51(2):120-8. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201000184. Epub 2010 Nov 12. J Basic Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21077122 Review.
-
Current Understanding of the Role of Neuronal Calcium Sensor 1 in Neurological Disorders.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Sep;56(9):6080-6094. doi: 10.1007/s12035-019-1497-2. Epub 2019 Feb 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30719643 Review.
Cited by
-
Disulfide Dimerization of Neuronal Calcium Sensor-1: Implications for Zinc and Redox Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 22;22(22):12602. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212602. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830487 Free PMC article.
-
The small GTPase ARF-1.2 is a regulator of unicellular tube formation in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Physiol Sci. 2019 Jan;69(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s12576-018-0617-5. Epub 2018 Apr 27. J Physiol Sci. 2019. PMID: 29704149 Free PMC article.
-
Rest Induces a Distinct Transcriptional Program in the Nervous System of the Exercised L. stagnalis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 20;26(14):6970. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146970. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725218 Free PMC article.
-
Partial inhibition of class III PI3K VPS-34 ameliorates motor aging and prolongs health span.PLoS Biol. 2023 Jul 11;21(7):e3002165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002165. eCollection 2023 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2023. PMID: 37432924 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Sensors in Neuronal Function and Dysfunction.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019 May 1;11(5):a035154. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a035154. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. PMID: 30833454 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fernandez-Chacon R. et al.. Synaptotagmin I functions as a calcium regulator of release probability. Nature 410, 41–49 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Yamauchi T. Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II–discovery, progress in a quarter of a century, and perspective: implication for learning and memory. Biological & pharmaceutical bulletin 28, 1342–1354 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

