Griffiths phase and long-range correlations in a biologically motivated visual cortex model
- PMID: 27435679
- PMCID: PMC4951650
- DOI: 10.1038/srep29561
Griffiths phase and long-range correlations in a biologically motivated visual cortex model
Abstract
Activity in the brain propagates as waves of firing neurons, namely avalanches. These waves' size and duration distributions have been experimentally shown to display a stable power-law profile, long-range correlations and 1/f (b) power spectrum in vivo and in vitro. We study an avalanching biologically motivated model of mammals visual cortex and find an extended critical-like region - a Griffiths phase - characterized by divergent susceptibility and zero order parameter. This phase lies close to the expected experimental value of the excitatory postsynaptic potential in the cortex suggesting that critical be-havior may be found in the visual system. Avalanches are not perfectly power-law distributed, but it is possible to collapse the distributions and define a cutoff avalanche size that diverges as the network size is increased inside the critical region. The avalanches present long-range correlations and 1/f (b) power spectrum, matching experiments. The phase transition is analytically determined by a mean-field approximation.
Figures
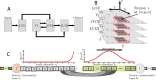
 , of choosing a presynaptic axonal compartment, ak, of any neuron is exponential such that most of the synapses start from the end of the axon (left). The probability,
, of choosing a presynaptic axonal compartment, ak, of any neuron is exponential such that most of the synapses start from the end of the axon (left). The probability,  , of choosing a dendritic postsynaptic compartment, dm, is Gaussian with mean 50 and standard deviation 10, so that most of the synapses lay in the middle of the dendrite (right).
, of choosing a dendritic postsynaptic compartment, dm, is Gaussian with mean 50 and standard deviation 10, so that most of the synapses lay in the middle of the dendrite (right).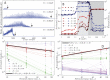
 ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ) indicate ρ and blue squares (
) indicate ρ and blue squares ( ,
,  ,
,  ,
,  ) indicate χρ; the larger L the darker the color shade. White background indicate the inactive phase, light gray background indicates the critical (Griffiths) phase with diverging χρ and dark gray background indicates the percolating phase. Panels C,D: FSS of ρ order parameter yielding scaling exponent β/ν⊥ = 0.55(3) – Equation (4) – and FSS of χρ yielding scaling exponent γ/ν⊥ = 3.1(1) – Equation (5); fits performed on the transition point Ec = 1.19 mV; (
) indicate χρ; the larger L the darker the color shade. White background indicate the inactive phase, light gray background indicates the critical (Griffiths) phase with diverging χρ and dark gray background indicates the percolating phase. Panels C,D: FSS of ρ order parameter yielding scaling exponent β/ν⊥ = 0.55(3) – Equation (4) – and FSS of χρ yielding scaling exponent γ/ν⊥ = 3.1(1) – Equation (5); fits performed on the transition point Ec = 1.19 mV; ( ) inactive phase, (
) inactive phase, ( ) critical phase, (
) critical phase, ( ) and (
) and ( ) percolating phases. Vertical bars are standard deviation and dotted lines are only guides to the eyes.
) percolating phases. Vertical bars are standard deviation and dotted lines are only guides to the eyes.
 for many E: (
for many E: ( ) inactive phase, (
) inactive phase, ( ) critical phase, (
) critical phase, ( ) and (
) and ( ) percolating phases. Note the bump around avalanches of size Nc ≈ 200 for E = 1.88 mV (
) percolating phases. Note the bump around avalanches of size Nc ≈ 200 for E = 1.88 mV ( ); this bump reveals the internal structure of the network (see text for discussion). The light gray background highlights the range of avalanche size s in which all phases have PL-shaped distributions. Panel A inset: avalanche distributions for the critical phase (E = 1.15 mV) for increasing L. Panel B: avalanche cumulative distributions
); this bump reveals the internal structure of the network (see text for discussion). The light gray background highlights the range of avalanche size s in which all phases have PL-shaped distributions. Panel A inset: avalanche distributions for the critical phase (E = 1.15 mV) for increasing L. Panel B: avalanche cumulative distributions  corresponding to panel A inset, E = 1.15 mV (the critical phase), for increasing L. Solid line is the fit of Equation (11) used to estimate Z(L = 20) and α = 1.4(1). Panel B inset: scaling law of Z ∼ LD for E = 1.15 mV yielding D = 1.0(1); this scaling holds inside the whole critical phase. Avalanche distributions for the other phases have different D and are presented in Fig. 4.
corresponding to panel A inset, E = 1.15 mV (the critical phase), for increasing L. Solid line is the fit of Equation (11) used to estimate Z(L = 20) and α = 1.4(1). Panel B inset: scaling law of Z ∼ LD for E = 1.15 mV yielding D = 1.0(1); this scaling holds inside the whole critical phase. Avalanche distributions for the other phases have different D and are presented in Fig. 4.
 . All the PL exponents were checked using Maximum Likelihood test (see Supplementary Material).
. All the PL exponents were checked using Maximum Likelihood test (see Supplementary Material).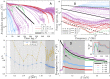
 ) inactive phase, (
) inactive phase, ( ) critical phase, (
) critical phase, ( ) and (
) and ( ) percolating phases. The bold lines show the exponential cutoff fit of the autocorrelation for E = 1.6 mV giving τ = 16.2 ts (A); and the fit S(f) ∼ f−b giving b = 0.97(5) for E = 1.15 mV (critical phase), b = 0.74(4) for E = 1.6 mV and b = 0.20(2) for E = 2 mV (weakly percolating phase) as examples (B). Notice how the curves’ slope in panel B smoothly vary and yield b ≈ 1 inside the GP (see panel C too). Panel C: Power spectrum and DFA exponents versus E inside and close to the GP. b is the avalanches power spectrum exponent and g is the DFA exponent of the activity time series (of Fig. 2A). Notice that b ≈ 1 and
) percolating phases. The bold lines show the exponential cutoff fit of the autocorrelation for E = 1.6 mV giving τ = 16.2 ts (A); and the fit S(f) ∼ f−b giving b = 0.97(5) for E = 1.15 mV (critical phase), b = 0.74(4) for E = 1.6 mV and b = 0.20(2) for E = 2 mV (weakly percolating phase) as examples (B). Notice how the curves’ slope in panel B smoothly vary and yield b ≈ 1 inside the GP (see panel C too). Panel C: Power spectrum and DFA exponents versus E inside and close to the GP. b is the avalanches power spectrum exponent and g is the DFA exponent of the activity time series (of Fig. 2A). Notice that b ≈ 1 and  inside the critical region indicating long-range temporal correlations of both the avalanche time series and the spiking activity of the network. Panel D: Activity propagation time T as function of E for many L; solid line indicates the asymptotic behavior of T. Panel D inset: collapse plot
inside the critical region indicating long-range temporal correlations of both the avalanche time series and the spiking activity of the network. Panel D: Activity propagation time T as function of E for many L; solid line indicates the asymptotic behavior of T. Panel D inset: collapse plot  yielding μ = 0.9(1). Arrows indicate the minimum of T, vertical bars are standard deviation, light gray is the GP and dark gray is the weakly percolating phase. See Supplementary Material for more details about T.
yielding μ = 0.9(1). Arrows indicate the minimum of T, vertical bars are standard deviation, light gray is the GP and dark gray is the weakly percolating phase. See Supplementary Material for more details about T.References
-
- Chialvo D. R., Balenzuela P. & Fraiman D. The brain: What is critical about it? AIP Conf. Proc. 1028, 28, 10.1063/1.2965095 (2008). - DOI
-
- Turing A. M. Computing machines and intelligence. Mind 59, 433–460 (1950).
-
- Chialvo D. R. Emergent complex neural dynamics. Nat. Phys. 6, 744–750 (2010).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

