Bacterial community characterization of water and intestine of the shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris in a biofloc system
- PMID: 27435866
- PMCID: PMC4952143
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-016-0770-z
Bacterial community characterization of water and intestine of the shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris in a biofloc system
Abstract
Background: Biofloc technology (BFT), a rearing method with little or no water exchange, is gaining popularity in aquaculture. In the water column, such systems develop conglomerates of microbes, algae and protozoa, together with detritus and dead organic particles. The intensive microbial community presents in these systems can be used as a pond water quality treatment system, and the microbial protein can serve as a feed additive. The current problem with BFT is the difficulty of controlling its bacterial community composition for both optimal water quality and optimal shrimp health. The main objective of the present study was to investigate microbial diversity of samples obtained from different culture environments (Biofloc technology and clear seawater) as well as from the intestines of shrimp reared in both environments through high-throughput sequencing technology.
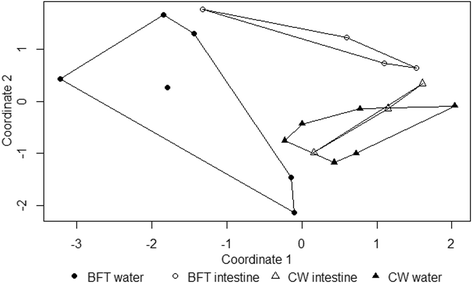
Results: Analyses of the bacterial community identified in water from BFT and "clear seawater" (CW) systems (control) containing the shrimp Litopenaeus stylirostris revealed large differences in the frequency distribution of operational taxonomic units (OTUs). Four out of the five most dominant bacterial communities were different in both culture methods. Bacteria found in great abundance in BFT have two principal characteristics: the need for an organic substrate or nitrogen sources to grow and the capacity to attach to surfaces and co-aggregate. A correlation was found between bacteria groups and physicochemical and biological parameters measured in rearing tanks. Moreover, rearing-water bacterial communities influenced the microbiota of shrimp. Indeed, the biofloc environment modified the shrimp intestine microbiota, as the low level (27 %) of similarity between intestinal bacterial communities from the two treatments.
Conclusion: This study provides the first information describing the complex biofloc microbial community, which can help to understand the environment-microbiota-host relationship in this rearing system.
Keywords: Bacterial communities; Biofloc; Clear sea water; Culture environment; Microbiota; Shrimp.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Carbon: Nitrogen (C:N) ratio level variation influences microbial community of the system and growth as well as immunity of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) in biofloc based culture system.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018 Oct;81:329-337. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2018.07.035. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30016684
-
Effect of stock density on the microbial community in biofloc water and Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) gut microbiota.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 May;103(10):4241-4252. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-09773-4. Epub 2019 Apr 5. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30953119
-
White spot syndrome virus (WSSV) disturbs the intestinal microbiota of shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) reared in biofloc and clear seawater.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Sep;104(18):8007-8023. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10816-4. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32789745
-
A Review: Microbes and Their Effect on Growth Performance of Litopenaeus vannamei (White Leg Shrimps) during Culture in Biofloc Technology System.Microorganisms. 2024 May 17;12(5):1013. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12051013. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38792842 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofloc technology and immune response of penaeid shrimp: A meta-analysis and meta-regression.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023 Jul;138:108805. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108805. Epub 2023 May 9. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37169111 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Chitosan-Gentamicin Conjugate Supplement on Non-Specific Immunity, Aquaculture Water, Intestinal Histology and Microbiota of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei).Mar Drugs. 2020 Aug 10;18(8):419. doi: 10.3390/md18080419. Mar Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32785070 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Probiotic Effects on the Growth Performance and Microbiome of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in a High-Density Biofloc System.Aquac Nutr. 2025 Jan 8;2025:5868806. doi: 10.1155/anu/5868806. eCollection 2025. Aquac Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39816909 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights into the Mechanism of Action of PirAB from Vibrio Parahaemolyticus.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Mar 30;14(4):243. doi: 10.3390/toxins14040243. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35448852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Penicillin Binding Protein from Pediococcus acidilactici Isolated from Nuruk for Food Biopreservative.Iran J Public Health. 2018 Nov;47(11):1653-1659. Iran J Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30581780 Free PMC article.
-
Improvement of hybrid grouper (Epinephelus fuscoguttatus ♀ × E. lanceolatus ♂) by enzyme-digested poultry by-product: Growth performance, amino acid and peptide transport capacity, and intestinal morphology.Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 19;9:955734. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.955734. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35928839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avnimelech Y. Biofloc Technology - a practical guide book. Baton Rouge: The World Aquaculture Society; 2009.
-
- Aguilera-Rivera D, Prieto-Davo A, Escalante K, Chavez C, Cuzon G, Gaxiola G. Probiotic effect of floc on Vibrios in the pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture. 2014;424:215–9. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.01.008. - DOI
-
- Ekasari J, Azhar MH, Surawidjaja EH, Nuryati S, De Schryver P, Bossier P. Immune response and disease resistance of shrimp fed biofloc grown on different carbon sources. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014;41(2):332–39. - PubMed
-
- Zhao P, Huang J, Wang XH, Song XL, Yang CH, Zhang XG, Wang GC. The application of bioflocs technology in high-intensive, zero exchange farming systems of Marsupenaeus japonicas. Aquaculture. 2012;354:97–106. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2012.03.034. - DOI
-
- Xu WJ, Pan LQ. Enhancement of immune response and antioxidant status of Litopenaeus vannamei juvenile in biofloc-based culture tanks manipulating high C/N ratio of feed input. Aquaculture. 2013;412:117–24. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2013.07.017. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

