Endoleak detection using single-acquisition split-bolus dual-energy computer tomography (DECT)
- PMID: 27436027
- PMCID: PMC5334388
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-016-4480-6
Endoleak detection using single-acquisition split-bolus dual-energy computer tomography (DECT)
Abstract
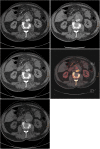
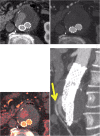
Objectives: To assess a single-phase, dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) with a split-bolus technique and reconstruction of virtual non-enhanced images for the detection of endoleaks after endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR).
Methods: Fifty patients referred for routine follow-up post-EVAR CT and a history of at least one post-EVAR follow-up CT examination using our standard biphasic (arterial and venous phase) routine protocol (which was used as the reference standard) were included in this prospective trial. An in-patient comparison and an analysis of the split-bolus protocol and the previously used double-phase protocol were performed with regard to differences in diagnostic accuracy, radiation dose, and image quality.
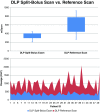
Results: The analysis showed a significant reduction of radiation dose of up to 42 %, using the single-acquisition split-bolus protocol, while maintaining a comparable diagnostic accuracy (primary endoleak detection rate of 96 %). Image quality between the two protocols was comparable and only slightly inferior for the split-bolus scan (2.5 vs. 2.4).
Conclusions: Using the single-acquisition, split-bolus approach allows for a significant dose reduction while maintaining high image quality, resulting in effective endoleak identification.
Key points: • A single-acquisition, split-bolus approach allows for a significant dose reduction. • Endoleak development is the most common complication after endovascular aortic repair (EVAR). • CT angiography is the imaging modality of choice for aortic aneurysm evaluation.
Keywords: Aneurysm; Angiography; Aorta; Computed tomography; Endoleak.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic CT angiography after abdominal aortic endovascular aneurysm repair: influence of enhancement patterns and optimal bolus timing on endoleak detection.Radiology. 2013 Sep;268(3):890-9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.13120197. Epub 2013 Apr 11. Radiology. 2013. PMID: 23579050
-
Dynamic CT angiography after abdominal aortic endovascular aneurysm repair: differences in contrast agent dynamics in the aorta and endoleaks--preliminary results.J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012 Jun;23(6):744-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2012.02.008. Epub 2012 Apr 10. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012. PMID: 22494657
-
Dual-energy computed tomography after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair: the role of hard plaque imaging for endoleak detection.Eur Radiol. 2014 Oct;24(10):2449-57. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3266-y. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Eur Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24965507
-
A meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of dual-energy computed tomography for endoleak detection after endovascular aneurysm repair.Eur Radiol. 2025 Jun 7. doi: 10.1007/s00330-025-11717-8. Online ahead of print. Eur Radiol. 2025. PMID: 40483293 Review.
-
Dual-energy computed tomography imaging of the aorta after endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm.Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2010 Aug;31(4):292-300. doi: 10.1053/j.sult.2010.05.003. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2010. PMID: 20691929 Review.
Cited by
-
Surveillance Imaging following Endovascular Aneurysm Repair: State of the Art.Semin Intervent Radiol. 2020 Oct;37(4):356-364. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1715882. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2020. PMID: 33041481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endotension: twenty years of a controversial term.CVIR Endovasc. 2021 Jun 5;4(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s42155-021-00238-2. CVIR Endovasc. 2021. PMID: 34089419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Endovascular aortic repair of endoleaks : Diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes].Radiologie (Heidelb). 2022 Jul;62(7):592-600. doi: 10.1007/s00117-022-01033-3. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Radiologie (Heidelb). 2022. PMID: 35736998 Free PMC article. Review. German.
-
Comparing Arterial- and Venous-Phase Acquisition for Optimization of Virtual Noncontrast Images From Dual-Energy Computed Tomography Angiography.J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2019 Sep/Oct;43(5):770-774. doi: 10.1097/RCT.0000000000000903. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2019. PMID: 31425308 Free PMC article.
-
Dual energy CT in clinical routine: how it works and how it adds value.Emerg Radiol. 2021 Feb;28(1):103-117. doi: 10.1007/s10140-020-01785-2. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Emerg Radiol. 2021. PMID: 32483665 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

