Rapid delayed growth of ruptured supraclinoid blister aneurysm after successful flow diverting stent treatment
- PMID: 27436031
- PMCID: PMC4964228
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-012506
Rapid delayed growth of ruptured supraclinoid blister aneurysm after successful flow diverting stent treatment
Abstract
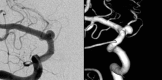
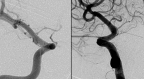
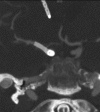
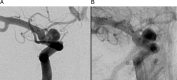
A 62-year-old woman presented with a subarachnoid hemorrhage secondary to a ruptured right supraclinoid internal carotid artery blister aneurysm. She was treated in an emergent fashion with two flow diverting pipeline embolization devices (PED) deployed in a telescoping fashion. CT angiography performed for unrelated reasons at 7 months showed successful treatment of the aneurysm without evidence of residual aneurysm. However, a follow-up digital subtraction angiogram performed at 9 months showed a large aneurysm in a modified position compared with the original aneurysm. This is the first case of rapid regrowth of a supraclinoid blister aneurysm after successful treatment with a PED, and demonstrates the need for close follow-up for similar aneurysms treated with this novel device.
Keywords: Aneurysm; Device; Flow Diverter; Subarachnoid.
2016 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Linfante I, Mayich M, Sonig A et al. . Flow diversion with pipeline embolic device as treatment of subarachnoid hemorrhage secondary to blister aneurysms: Dual-center experience and review of the literature. J Neurointerv Surg Published Online First: 13 Apr 2016. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012287 10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012287 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
