PETModule: a motif module based approach for enhancer target gene prediction
- PMID: 27436110
- PMCID: PMC4951774
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30043
PETModule: a motif module based approach for enhancer target gene prediction
Abstract
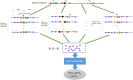
The identification of enhancer-target gene (ETG) pairs is vital for the understanding of gene transcriptional regulation. Experimental approaches such as Hi-C have generated valuable resources of ETG pairs. Several computational methods have also been developed to successfully predict ETG interactions. Despite these progresses, high-throughput experimental approaches are still costly and existing computational approaches are still suboptimal and not easy to apply. Here we developed a motif module based approach called PETModule that predicts ETG pairs. Tested on eight human cell types and two mouse cell types, we showed that a large number of our predictions were supported by Hi-C and/or ChIA-PET experiments. Compared with two recently developed approaches for ETG pair prediction, we shown that PETModule had a much better recall, a similar or better F1 score, and a larger area under the receiver operating characteristic curve. The PETModule tool is freely available at http://hulab.ucf.edu/research/projects/PETModule/.
Figures
References
-
- Blackwood E. M. & Kadonaga J. T. Going the distance: a current view of enhancer action. Science 281, 60–63 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Maston G. A., Evans S. K. & Green M. R. Transcriptional regulatory elements in the human genome. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 7, 29–59 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Latchman D. S. Transcription factors: an overview. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology 29, 1305–1312 (1997). - PubMed
-
- Lenhard B. & Wasserman W. W. TFBS: Computational framework for transcription factor binding site analysis. Bioinformatics 18, 1135–1136 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources