De novo nonsense and frameshift variants of TCF20 in individuals with intellectual disability and postnatal overgrowth
- PMID: 27436265
- PMCID: PMC5117939
- DOI: 10.1038/ejhg.2016.90
De novo nonsense and frameshift variants of TCF20 in individuals with intellectual disability and postnatal overgrowth
Abstract
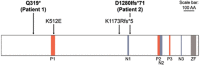
Recently, germline variants of the transcriptional co-regulator gene TCF20 have been implicated in the aetiology of autism spectrum disorders (ASD). However, the knowledge about the associated clinical picture remains fragmentary. In this study, two individuals with de novo TCF20 sequence variants were identified in a cohort of 313 individuals with intellectual disability of unknown aetiology, which was analysed by whole exome sequencing using a child-parent trio design. Both detected variants - one nonsense and one frameshift variant - were truncating. A comprehensive clinical characterisation of the patients yielded mild intellectual disability, postnatal tall stature and macrocephaly, obesity and muscular hypotonia as common clinical signs while ASD was only present in one proband. The present report begins to establish the clinical picture of individuals with de novo nonsense and frameshift variants of TCF20 which includes features such as proportionate overgrowth and muscular hypotonia. Furthermore, intellectual disability/developmental delay seems to be fully penetrant amongst known individuals with de novo nonsense and frameshift variants of TCF20, whereas ASD is shown to be incompletely penetrant. The transcriptional co-regulator gene TCF20 is hereby added to the growing number of genes implicated in the aetiology of both ASD and intellectual disability. Furthermore, such de novo variants of TCF20 may represent a novel differential diagnosis in the overgrowth syndrome spectrum.
Figures

References
-
- Gray PA, Fu H, Luo P et al: Mouse brain organization revealed through direct genome-scale Tf expression analysis. Science 2004; 306: 2255–2257. - PubMed
-
- Lein ES, Hawrylycz MJ, Ao N et al: Genome-wide atlas of gene expression in the adult mouse brain. Nature 2007; 445: 168–176. - PubMed
-
- Rekdal C, Sjottem E, Johansen T: The nuclear factor SPBP contains different functional domains and stimulates the activity of various transcriptional activators. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 40288–40300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

