Quadrupedal Robot Locomotion: A Biologically Inspired Approach and Its Hardware Implementation
- PMID: 27436997
- PMCID: PMC4942632
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/5615618
Quadrupedal Robot Locomotion: A Biologically Inspired Approach and Its Hardware Implementation
Abstract
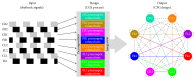
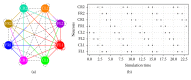
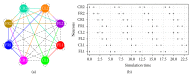
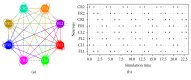
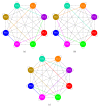
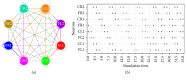
A bioinspired locomotion system for a quadruped robot is presented. Locomotion is achieved by a spiking neural network (SNN) that acts as a Central Pattern Generator (CPG) producing different locomotion patterns represented by their raster plots. To generate these patterns, the SNN is configured with specific parameters (synaptic weights and topologies), which were estimated by a metaheuristic method based on Christiansen Grammar Evolution (CGE). The system has been implemented and validated on two robot platforms; firstly, we tested our system on a quadruped robot and, secondly, on a hexapod one. In this last one, we simulated the case where two legs of the hexapod were amputated and its locomotion mechanism has been changed. For the quadruped robot, the control is performed by the spiking neural network implemented on an Arduino board with 35% of resource usage. In the hexapod robot, we used Spartan 6 FPGA board with only 3% of resource usage. Numerical results show the effectiveness of the proposed system in both cases.
Figures








References
-
- Full R. J., Koditschek D. E. Templates and anchors: neuromechanical hypotheses of legged locomotion on land. The Journal of Experimental Biology. 1999;202(23):3325–3332. - PubMed
-
- Kimura H., Shimoyama I., Miura H. Dynamics in the dynamicwalk of a quadruped robot. International Journal of Robotics Research. 2003;4(2):187–202.
-
- Scott L. H. Central pattern generator. Current Biology. 2000;10(2):176–177.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

