Integrating Heterogeneous Biomedical Data for Cancer Research: the CARPEM infrastructure
- PMID: 27437039
- PMCID: PMC4941838
- DOI: 10.4338/ACI-2015-09-RA-0125
Integrating Heterogeneous Biomedical Data for Cancer Research: the CARPEM infrastructure
Abstract
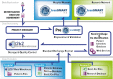
Cancer research involves numerous disciplines. The multiplicity of data sources and their heterogeneous nature render the integration and the exploration of the data more and more complex. Translational research platforms are a promising way to assist scientists in these tasks. In this article, we identify a set of scientific and technical principles needed to build a translational research platform compatible with ethical requirements, data protection and data-integration problems. We describe the solution adopted by the CARPEM cancer research program to design and deploy a platform able to integrate retrospective, prospective, and day-to-day care data. We designed a three-layer architecture composed of a data collection layer, a data integration layer and a data access layer. We leverage a set of open-source resources including i2b2 and tranSMART.
Keywords: Data integration; medical information systems; translational medicine; translational research platform.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in the research
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Use of Translational Research Platforms in Clinical and Biomedical Data Exploration.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;988:301-311. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-56246-9_25. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28971409 Review.
-
The ONCO-I2b2 project: integrating biobank information and clinical data to support translational research in oncology.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2011;169:887-91. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2011. PMID: 21893874
-
Data Integration for Future Medicine (DIFUTURE).Methods Inf Med. 2018 Jul;57(S 01):e57-e65. doi: 10.3414/ME17-02-0022. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Methods Inf Med. 2018. PMID: 30016812 Free PMC article.
-
Enabling Agile Clinical and Translational Data Warehousing: Platform Development and Evaluation.JMIR Med Inform. 2020 Jul 21;8(7):e15918. doi: 10.2196/15918. JMIR Med Inform. 2020. PMID: 32706673 Free PMC article.
-
An Architecture for Translational Cancer Research As Exemplified by the German Cancer Consortium.JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2018 Dec;2:1-8. doi: 10.1200/CCI.17.00062. JCO Clin Cancer Inform. 2018. PMID: 30652543 Review.
Cited by
-
Labeling for Big Data in radiation oncology: The Radiation Oncology Structures ontology.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 19;13(1):e0191263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191263. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29351341 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning and Radiomics predict complete response after neo-adjuvant chemoradiation for locally advanced rectal cancer.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 22;8(1):12611. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30657-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30135549 Free PMC article.
-
Usability and Suitability of the Omics-Integrating Analysis Platform tranSMART for Translational Research and Education.Appl Clin Inform. 2017 Oct;8(4):1173-1183. doi: 10.4338/ACI-2017-05-RA-0085. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Appl Clin Inform. 2017. PMID: 29270954 Free PMC article.
-
Data and knowledge management in translational research: implementation of the eTRIKS platform for the IMI OncoTrack consortium.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Apr 1;20(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2748-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30935364 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Multimodal Radiation Therapy Data into i2b2.Appl Clin Inform. 2018 Apr;9(2):377-390. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1651497. Epub 2018 May 30. Appl Clin Inform. 2018. PMID: 29847842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hagemann IS, Cottrell CE, Lockwood CM. Design of targeted, capture-based, next generation sequencing tests for precision cancer therapy. Cancer Genet 2013; 206(12):420–431. - PubMed
-
- Chang F, Li MM. Clinical application of amplicon-based next-generation sequencing in cancer. Cancer Genet 2013; 206(12):413–419. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources