Structural organization of the inactive X chromosome in the mouse
- PMID: 27437574
- PMCID: PMC5443622
- DOI: 10.1038/nature18589
Structural organization of the inactive X chromosome in the mouse
Abstract
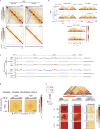
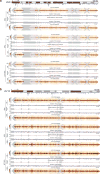
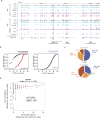
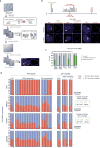
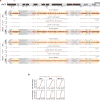
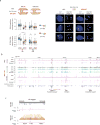
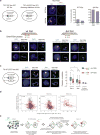
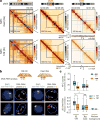
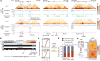
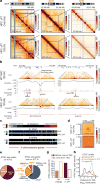
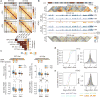
X-chromosome inactivation (XCI) involves major reorganization of the X chromosome as it becomes silent and heterochromatic. During female mammalian development, XCI is triggered by upregulation of the non-coding Xist RNA from one of the two X chromosomes. Xist coats the chromosome in cis and induces silencing of almost all genes via its A-repeat region, although some genes (constitutive escapees) avoid silencing in most cell types, and others (facultative escapees) escape XCI only in specific contexts. A role for Xist in organizing the inactive X (Xi) chromosome has been proposed. Recent chromosome conformation capture approaches have revealed global loss of local structure on the Xi chromosome and formation of large mega-domains, separated by a region containing the DXZ4 macrosatellite. However, the molecular architecture of the Xi chromosome, in both the silent and expressed regions,remains unclear. Here we investigate the structure, chromatin accessibility and expression status of the mouse Xi chromosome in highly polymorphic clonal neural progenitors (NPCs) and embryonic stem cells. We demonstrate a crucial role for Xist and the DXZ4-containing boundary in shaping Xi chromosome structure using allele-specific genome-wide chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) analysis, an assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high throughput sequencing (ATAC-seq) and RNA sequencing. Deletion of the boundary disrupts mega-domain formation, and induction of Xist RNA initiates formation of the boundary and the loss of DNA accessibility. We also show that in NPCs, the Xi chromosome lacks active/inactive compartments and topologically associating domains (TADs), except around genes that escape XCI. Escapee gene clusters display TAD-like structures and retain DNA accessibility at promoter-proximal and CTCF-binding sites. Furthermore, altered patterns of facultative escape genes indifferent neural progenitor clones are associated with the presence of different TAD-like structures after XCI. These findings suggest a key role for transcription and CTCF in the formation of TADs in the context of the Xi chromosome in neural progenitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests. Readers are welcome to comment on the online version of the paper.
Figures


References
-
- Wutz A, Rasmussen TP, Jaenisch R. Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA. Nature Genet. 2002;30:167–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

