A multi-modal parcellation of human cerebral cortex
- PMID: 27437579
- PMCID: PMC4990127
- DOI: 10.1038/nature18933
A multi-modal parcellation of human cerebral cortex
Abstract
Understanding the amazingly complex human cerebral cortex requires a map (or parcellation) of its major subdivisions, known as cortical areas. Making an accurate areal map has been a century-old objective in neuroscience. Using multi-modal magnetic resonance images from the Human Connectome Project (HCP) and an objective semi-automated neuroanatomical approach, we delineated 180 areas per hemisphere bounded by sharp changes in cortical architecture, function, connectivity, and/or topography in a precisely aligned group average of 210 healthy young adults. We characterized 97 new areas and 83 areas previously reported using post-mortem microscopy or other specialized study-specific approaches. To enable automated delineation and identification of these areas in new HCP subjects and in future studies, we trained a machine-learning classifier to recognize the multi-modal 'fingerprint' of each cortical area. This classifier detected the presence of 96.6% of the cortical areas in new subjects, replicated the group parcellation, and could correctly locate areas in individuals with atypical parcellations. The freely available parcellation and classifier will enable substantially improved neuroanatomical precision for studies of the structural and functional organization of human cerebral cortex and its variation across individuals and in development, aging, and disease.
Figures
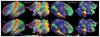
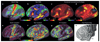
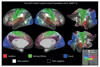
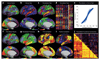
Comment in
-
Systems neuroscience: A modern map of the human cerebral cortex.Nature. 2016 Aug 11;536(7615):152-4. doi: 10.1038/nature18914. Epub 2016 Jul 20. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27437585 No abstract available.
-
Human Cerebral Cortex Map 2.0.Neurosurgery. 2016 Dec;79(6):N16-N17. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000508603.53941.07. Neurosurgery. 2016. PMID: 27861409 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brodmann K. Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Grosshirnrinde in ihren Prinzipien dargestellt auf Grund des Zellenbaues. J.A. Barth; 1909.
- Garey LJ, translator. Brodmann’s Localization in the Cerebral Cortex. Smith Gordon; 1994.
-
- Felleman DJ, Van Essen DC. Distributed hierarchical processing in the primate cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex. 1991;1:1–47. - PubMed
-
- Nieuwenhuys R. The myeloarchitectonic studies on the human cerebral cortex of the Vogt–Vogt school, and their significance for the interpretation of functional neuroimaging data. Brain Struct Funct. 2013;218:303–352. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

