Genetic dissection of the Transcription Factor code controlling serial specification of muscle identities in Drosophila
- PMID: 27438571
- PMCID: PMC4954755
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.14979
Genetic dissection of the Transcription Factor code controlling serial specification of muscle identities in Drosophila
Abstract
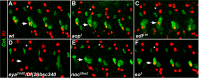
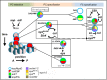
Each Drosophila muscle is seeded by one Founder Cell issued from terminal division of a Progenitor Cell (PC). Muscle identity reflects the expression by each PC of a specific combination of identity Transcription Factors (iTFs). Sequential emergence of several PCs at the same position raised the question of how developmental time controlled muscle identity. Here, we identified roles of Anterior Open and ETS domain lacking in controlling PC birth time and Eyes absent, No Ocelli, and Sine oculis in specifying PC identity. The windows of transcription of these and other TFs in wild type and mutant embryos, revealed a cascade of regulation integrating time and space, feed-forward loops and use of alternative transcription start sites. These data provide a dynamic view of the transcriptional control of muscle identity in Drosophila and an extended framework for studying interactions between general myogenic factors and iTFs in evolutionary diversification of muscle shapes.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Transcription Factors; developmental biology; myogenesis; regulatory networks; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Tup/Islet1 integrates time and position to specify muscle identity in Drosophila.Development. 2012 Oct;139(19):3572-82. doi: 10.1242/dev.083410. Development. 2012. PMID: 22949613
-
Combinatorial coding of Drosophila muscle shape by Collier and Nautilus.Dev Biol. 2012 Mar 1;363(1):27-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.12.018. Epub 2011 Dec 20. Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22200594
-
ladybird determines cell fate decisions during diversification of Drosophila somatic muscles.Development. 1998 Sep;125(18):3699-708. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.18.3699. Development. 1998. PMID: 9716535
-
Diversification of muscle types in Drosophila: upstream and downstream of identity genes.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012;98:277-301. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-386499-4.00011-2. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2012. PMID: 22305167 Review.
-
Muscle pattern diversification in Drosophila: the story of imaginal myogenesis.Bioessays. 1999 Jun;21(6):486-98. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199906)21:6<486::AID-BIES5>3.0.CO;2-M. Bioessays. 1999. PMID: 10402955 Review.
Cited by
-
SIX1 reprograms myogenic transcription factors to maintain the rhabdomyosarcoma undifferentiated state.Cell Rep. 2022 Feb 1;38(5):110323. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110323. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35108532 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of transcriptional (re)-programming of syncytial nuclei in developing muscles.BMC Biol. 2017 Jun 9;15(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0386-2. BMC Biol. 2017. PMID: 28599653 Free PMC article.
-
Some molecular aspects of larval development in Paralithodes camtschaticus.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 29;20(4):e0322234. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322234. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40299921 Free PMC article.
-
Insights and perspectives on the enigmatic alary muscles of arthropods.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 15;11:1337708. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1337708. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38288343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple cis-regulatory modules ensure robust tup/islet1 function in dorsal muscle identity specification.Skelet Muscle. 2025 Aug 25;15(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13395-025-00392-4. Skelet Muscle. 2025. PMID: 40855345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bate M. The mesoderm and its derivatives. In: Bate M, Martinez Arias A, editors. The Development of Drosophila Melanogaster. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1993. pp. 1013–1090.
-
- Berger C, Urban J, Technau GM. Stage-specific inductive signals in the Drosophila neuroectoderm control the temporal sequence of neuroblast specification. Development. 2001;128:3243–3251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

