The World Health Organization Measles Programmatic Risk Assessment Tool-Romania, 2015
- PMID: 27439071
- PMCID: PMC9245689
- DOI: 10.1111/risa.12669
The World Health Organization Measles Programmatic Risk Assessment Tool-Romania, 2015
Abstract
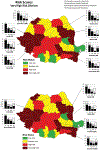
Despite global improvement in annual measles incidence and mortality since 2000, progress toward elimination goals has slowed. The World Health Organization (WHO) European Region (EUR) established a regional goal for measles and rubella elimination by 2015. Romania is one of 13 EUR countries in which measles remains endemic. To identify barriers to meeting programmatic targets and to aid in prioritizing efforts to strengthen measles elimination strategy implementation, the WHO and U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention developed a measles programmatic risk assessment tool that uses routinely collected data to estimate district-level risk scores. The WHO measles programmatic risk assessment tool was used to identify high-risk areas in order to guide measles elimination program activities in Romania. Of the 42 districts in Romania, 27 (64%) were categorized as very high or high risk. Many of the very-high-risk districts were clustered in the western part of the country or were clustered around the capital Bucharest in the southeastern part of the country. The overall risk scores in the very-high-risk districts were driven primarily by poor surveillance quality and suboptimal population immunity. The measles risk assessment conducted in Romania was the first assessment to be completed in a European country. Annual assessments using the programmatic risk tool could provide valuable information for immunization program and surveillance staff at the national level and in each district to guide activities to enhance measles elimination efforts, such as strengthening routine immunization services, improving immunization campaign planning, and intensifying surveillance.
Keywords: Elimination; Romania; measles; outbreak; risk assessment.
© 2016 Society for Risk Analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests: None of the authors have a commercial or other financial interest associated with the information presented in this article.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Global Vaccine Action Plan 2011–2020, 2013.
-
- Perry RT, Murray JS, Gacic-Dobo M, Dabbagh A, Mulders MN, Strebel PM, Okwo-Bele JM, Rota PA, Goodson JL. Progress toward regional measles elimination—Worldwide, 2000–2014. Morbidity Mortality Weekly Report, 2015; 64(44):1246–1251. - PubMed
-
- Muscat M, Shefer A, Ben Mamou M, Spataru R, Jankovic D, Deshevoy S, Butler R, Pfeifer D. The state of measles and rubella in the WHO European Region, 2013. Clinical Micro-biology and Infection, 2014; 20(Suppl 5):12–18. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Regional Committee for Europe. Sixtieth session. Renewed commitment to elimination of measles and rubella and prevention of congenital rubella syndrome by 2015 and sustained support for polio-free status in the WHO European region 2010. Available at: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/119546/RC60_edoc15.pdf, Accessed December 11, 2015.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Implementing the ECDC Action Plan for Measles and Rubella. Available at: http://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications/Publications/measles-rubella-i..., Accessed March 3, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

