Unexpected properties of sRNA promoters allow feedback control via regulation of a two-component system
- PMID: 27439713
- PMCID: PMC5175337
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw642
Unexpected properties of sRNA promoters allow feedback control via regulation of a two-component system
Abstract
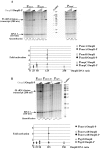
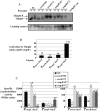
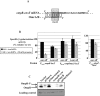
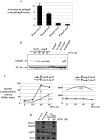
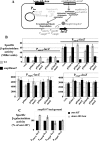
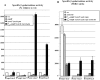
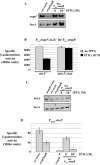
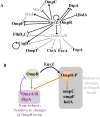
Two-component systems (TCS) and small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) are both widespread regulators of gene expression in bacteria. TCS are in most cases transcriptional regulators. A large class of sRNAs act as post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression that modulate the translation and/or stability of target-mRNAs. Many connections have been recently unraveled between these two types of regulators, resulting in mixed regulatory circuits with poorly characterized properties. This study focuses on the negative feedback circuit that exists between the EnvZ-OmpR TCS and the OmrA/B sRNAs. We have shown that OmpR directly activates transcription from the omrA and omrB promoters, allowing production of OmrA/B sRNAs that target multiple mRNAs, including the ompR-envZ mRNA. This control of ompR-envZ by the Omr sRNAs does not affect the amount of phosphorylated OmpR, i.e. the presumably active form of the regulator. Accordingly, expression of robust OmpR targets, such as the ompC or ompF porin genes, is not affected by OmrA/B. However, we find that several OmpR targets, including OmrA/B themselves, are sensitive to changing total OmpR levels. As a result, OmrA/B limit their own synthesis. These findings unravel an additional layer of control in the expression of some OmpR targets and suggest the existence of differential regulation within the OmpR regulon.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The 5' end of two redundant sRNAs is involved in the regulation of multiple targets, including their own regulator.Nucleic Acids Res. 2008 Dec;36(21):6781-94. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn742. Epub 2008 Oct 25. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008. PMID: 18953042 Free PMC article.
-
A phosphorylation site mutant of OmpR reveals different binding conformations at ompF and ompC.J Mol Biol. 2002 Jan 25;315(4):497-511. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.5222. J Mol Biol. 2002. PMID: 11812125
-
Remodelling of the Escherichia coli outer membrane by two small regulatory RNAs.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Jan;59(1):231-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04929.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16359331
-
Rewiring two-component signal transduction with small RNAs.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012 Apr;15(2):132-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.12.001. Epub 2011 Dec 23. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22197250 Review.
-
Integration of Bacterial Small RNAs in Regulatory Networks.Annu Rev Biophys. 2017 May 22;46:131-148. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-070816-034058. Annu Rev Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28532217 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of small base-pairing RNAs derived from diverse genomic loci.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020 Jul;1863(7):194524. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194524. Epub 2020 Mar 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2020. PMID: 32147527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small RNAs OmrA and OmrB promote class III flagellar gene expression by inhibiting the synthesis of anti-Sigma factor FlgM.RNA Biol. 2020 Jun;17(6):872-880. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2020.1733801. Epub 2020 Mar 5. RNA Biol. 2020. PMID: 32133913 Free PMC article.
-
Asymmetric regulation of quorum-sensing receptors drives autoinducer-specific gene expression programs in Vibrio cholerae.PLoS Genet. 2017 May 26;13(5):e1006826. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006826. eCollection 2017 May. PLoS Genet. 2017. PMID: 28552952 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing Escherichia coli's transcriptional response to different styrene exposure modes reveals novel toxicity and tolerance insights.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Apr 30;48(1-2):kuab019. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuab019. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33640981 Free PMC article.
-
Hfq influences ciprofloxacin accumulation in Escherichia coli independently of ompC and ompF post-transcriptional regulation.J Appl Genet. 2025 May;66(2):449-457. doi: 10.1007/s13353-025-00945-9. Epub 2025 Feb 8. J Appl Genet. 2025. PMID: 39920540
References
-
- Pratt L., Silhavy T. Porin regulon of Escherichia coli. In: Hoch J, Silhavy T, editors. Two-Component Signal Transduction. American Society for Microbiology; 1995. pp. 105–127.
-
- Pratt L.A., Hsing W., Gibson K.E., Silhavy T.J. From acids to osmZ: multiple factors influence synthesis of the OmpF and OmpC porins in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1996;20:911–917. - PubMed
-
- Kenney L.J. Structure/function relationships in OmpR and other winged-helix transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002;5:135–141. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

