Carfilzomib significantly improves the progression-free survival of high-risk patients in multiple myeloma
- PMID: 27439911
- PMCID: PMC5009511
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-707596
Carfilzomib significantly improves the progression-free survival of high-risk patients in multiple myeloma
Abstract
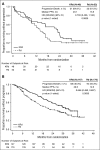
The presence of certain high-risk cytogenetic abnormalities, such as translocations (4;14) and (14;16) and deletion (17p), are known to have a negative impact on survival in multiple myeloma (MM). The phase 3 study ASPIRE (N = 792) demonstrated that progression-free survival (PFS) was significantly improved with carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd), compared with lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in relapsed MM. This preplanned subgroup analysis of ASPIRE was conducted to evaluate KRd vs Rd by baseline cytogenetics according to fluorescence in situ hybridization. Of 417 patients with known cytogenetic risk status, 100 patients (24%) were categorized with high-risk cytogenetics (KRd, n = 48; Rd, n = 52) and 317 (76%) were categorized with standard-risk cytogenetics (KRd, n = 147; Rd, n = 170). For patients with high-risk cytogenetics, treatment with KRd resulted in a median PFS of 23.1 months, a 9-month improvement relative to treatment with Rd. For patients with standard-risk cytogenetics, treatment with KRd led to a 10-month improvement in median PFS vs Rd. The overall response rates for KRd vs Rd were 79.2% vs 59.6% (high-risk cytogenetics) and 91.2% vs 73.5% (standard-risk cytogenetics); approximately fivefold as many patients with high- or standard-risk cytogenetics achieved a complete response or better with KRd vs Rd (29.2% vs 5.8% and 38.1% vs 6.5%, respectively). KRd improved but did not abrogate the poor prognosis associated with high-risk cytogenetics. This regimen had a favorable benefit-risk profile in patients with relapsed MM, irrespective of cytogenetic risk status, and should be considered a standard of care in these patients. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT01080391.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Response and progression-free survival according to planned treatment duration in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma treated with carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in the phase III ASPIRE study.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Apr 4;11(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0583-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29615082 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Carfilzomib-lenalidomide-dexamethasone vs lenalidomide-dexamethasone in relapsed multiple myeloma by previous treatment.Blood Cancer J. 2017 Apr 21;7(4):e554. doi: 10.1038/bcj.2017.31. Blood Cancer J. 2017. PMID: 28430175 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Health-Related Quality-of-Life Results From the Open-Label, Randomized, Phase III ASPIRE Trial Evaluating Carfilzomib, Lenalidomide, and Dexamethasone Versus Lenalidomide and Dexamethasone in Patients With Relapsed Multiple Myeloma.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Nov 10;34(32):3921-3930. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.66.9648. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27601539 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative efficacy of carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) versus bortezomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (VRd) in newly-diagnosed multiple myeloma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Hematol. 2024 Jul;99(7):1411-1414. doi: 10.1002/ajh.27314. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Am J Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38606993
-
Proteasome inhibitor-based therapy for treatment of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.Semin Oncol. 2017 Dec;44(6):381-384. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Semin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 29935899 Review.
Cited by
-
Interpreting clinical trial data in multiple myeloma: translating findings to the real-world setting.Blood Cancer J. 2018 Nov 9;8(11):109. doi: 10.1038/s41408-018-0141-0. Blood Cancer J. 2018. PMID: 30413684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilizing an Endogenous Progesterone Receptor Reporter Gene for Drug Screening and Mechanistic Study in Endometrial Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 6;14(19):4883. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194883. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230806 Free PMC article.
-
Response and progression-free survival according to planned treatment duration in patients with relapsed multiple myeloma treated with carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone (KRd) versus lenalidomide and dexamethasone (Rd) in the phase III ASPIRE study.J Hematol Oncol. 2018 Apr 4;11(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13045-018-0583-7. J Hematol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29615082 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of elderly patients with refractory/relapsed multiple myeloma: oral drugs adherence and the COVID-19 outbreak.Oncotarget. 2020 Nov 24;11(47):4371-4386. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27819. eCollection 2020 Nov 24. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 33316011 Free PMC article.
-
Carfilzomib, cyclophosphamide and dexamethasone for newly diagnosed, high-risk myeloma patients not eligible for transplant: a pooled analysis of two studies.Haematologica. 2021 Apr 1;106(4):1079-1085. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.243428. Haematologica. 2021. PMID: 32107329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stewart AK, Rajkumar SV, Dimopoulos MA, et al. ASPIRE Investigators. Carfilzomib, lenalidomide, and dexamethasone for relapsed multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(2):142–152. - PubMed
-
- Avet-Loiseau H, Attal M, Moreau P, et al. Genetic abnormalities and survival in multiple myeloma: the experience of the Intergroupe Francophone du Myélome. Blood. 2007;109(8):3489–3495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous