IQGAP1 Binds to Yes-associated Protein (YAP) and Modulates Its Transcriptional Activity
- PMID: 27440047
- PMCID: PMC5016668
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.732529
IQGAP1 Binds to Yes-associated Protein (YAP) and Modulates Its Transcriptional Activity
Abstract
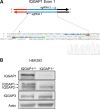
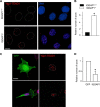
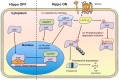
During development, the Hippo signaling pathway regulates key physiological processes, such as control of organ size, regeneration, and stem cell biology. Yes-associated protein (YAP) is a major transcriptional co-activator of the Hippo pathway. The scaffold protein IQGAP1 interacts with more than 100 binding partners to integrate diverse signaling pathways. In this study, we report that IQGAP1 binds to YAP and modulates its activity. IQGAP1 and YAP co-immunoprecipitated from cells. In vitro analysis with pure proteins demonstrated a direct interaction between IQGAP1 and YAP. Analysis with multiple fragments of each protein showed that the interaction occurs via the IQ domain of IQGAP1 and the TEAD-binding domain of YAP. The interaction between IQGAP1 and YAP has functional effects. Knock-out of endogenous IQGAP1 significantly increased the formation of nuclear YAP-TEAD complexes. Transcription assays were performed with IQGAP1-null mouse embryonic fibroblasts and HEK293 cells with IQGAP1 knockdown by CRISPR/Cas9. Quantification demonstrated that YAP-TEAD-mediated transcription in cells lacking IQGAP1 was significantly greater than in control cells. These data reveal that IQGAP1 binds to YAP and modulates its co-transcriptional function, suggesting that IQGAP1 participates in Hippo signaling.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; IQGAP1; cell signaling; protein complex; transcription factor; yes-associated protein (YAP).
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pannexin 1 crosstalk with the Hippo pathway in malignant melanoma.FEBS J. 2025 Apr;292(7):1633-1653. doi: 10.1111/febs.17396. Epub 2025 Jan 9. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 39786847
-
IQGAP1 participates in endothelial cell apoptosis and regulates atherosclerosis by targeting YAP.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 14;20(7):e0328345. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328345. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40658677 Free PMC article.
-
The PDZ-binding motif of Yes-associated protein is required for its co-activation of TEAD-mediated CTGF transcription and oncogenic cell transforming activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Jan 17;443(3):917-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.12.100. Epub 2013 Dec 28. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24380865
-
Angiomotin'g YAP into the nucleus for cell proliferation and cancer development.Sci Signal. 2013 Sep 3;6(291):pe27. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004573. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 24003252 Review.
-
YAP/TAZ for cancer therapy: opportunities and challenges (review).Int J Oncol. 2015 Apr;46(4):1444-52. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2015.2877. Epub 2015 Feb 5. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25652178 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of scaffold proteins in the heterogeneity of glioblastoma.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 7;22(1):477. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01809-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39375741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Haldol Targets IQGAP1 Pathway and Promotes Novel Partner Interactions in Glioblastoma Cell Lines.MicroPubl Biol. 2023 May 8;2023:10.17912/micropub.biology.000822. doi: 10.17912/micropub.biology.000822. eCollection 2023. MicroPubl Biol. 2023. PMID: 37228393 Free PMC article.
-
Scaffolding Protein IQGAP1 Is Dispensable, but Its Overexpression Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma via YAP1 Signaling.Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Mar 24;41(4):e00596-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00596-20. Print 2021 Mar 24. Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33526450 Free PMC article.
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation of the scaffold protein IQGAP1 in the MET pathway alters function.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 25;295(52):18105-18121. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015891. Epub 2020 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33087447 Free PMC article.
-
Hippo Signaling in the Liver - A Long and Ever-Expanding Story.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Mar 12;7:33. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2019.00033. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30931304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sudol M., Bork P., Einbond A., Kastury K., Druck T., Negrini M., Huebner K., and Lehman D. (1995) Characterization of the mammalian YAP (Yes-associated protein) gene and its role in defining a novel protein module, the WW domain. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 14733–14741 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

