Update on Clinical Strategies in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia from an ENT Point of View
- PMID: 27440131
- PMCID: PMC5426390
- DOI: 10.21053/ceo.2016.00318
Update on Clinical Strategies in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia from an ENT Point of View
Abstract
Objectives: Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is characterized by the presence of vascular malformations with an absence of capillaries between arteries and veins. One major manifestation site is the nasal mucous membrane where recurrent nosebleeds occur. Our clinical strategy to treat patients with HHT has the aim to reduce nasal bleeding long-term with minimal local and general side effects.
Methods: We describe staged diagnosis and therapy including individual medical treatments of 97 patients with HHT. The success of treatment is monitored with a systematic questionnaire.
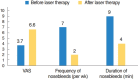
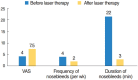
Results: The neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG) laser therapy remains standard treatment of choice with no major side effects despite the need for repeated treatment. In addition new treatment strategies like nasal occlusion, local drug therapy, and nasal septal splinting show initial success.
Conclusion: Improvement of the quality of life of HHT patients can be achieved by a multimodal concept. Several new treatment strategies like nasal septal splinting and nasal occlusion successfully expand the range of established methods. Further studies have to prove the safety and long-term effectiveness of the described individual medical treatments.
Keywords: Arteriovenous Malformations; Bevacizumab; Epistaxis; Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia; Nd:YAG Laser; Osler-Rendu-Weber Syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laser-Assisted Control of Epistaxis in Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: A Systematic Review.Lasers Surg Med. 2020 Apr;52(4):293-300. doi: 10.1002/lsm.23147. Epub 2019 Aug 22. Lasers Surg Med. 2020. PMID: 31441079 Free PMC article.
-
[Bevacizumab: a new success in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia].Rev Med Interne. 2015 Sep;36(9):623-5. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2014.11.004. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Rev Med Interne. 2015. PMID: 25595875 French.
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Nosebleed (Epistaxis).Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(1_suppl):S1-S38. doi: 10.1177/0194599819890327. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 31910111
-
Clinical Practice Guideline: Nosebleed (Epistaxis) Executive Summary.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jan;162(1):8-25. doi: 10.1177/0194599819889955. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 31910122 Review.
-
Satisfactory treatment of mucocutaneous lesions in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia patients with dual pulsed dye laser and neodymium: yttrium-aluminum-garnet.Dermatol Ther. 2021 Nov;34(6):e15124. doi: 10.1111/dth.15124. Epub 2021 Sep 13. Dermatol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34486206
Cited by
-
Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Success of the Osler Calendar for Documentation of Treatment and Course of Disease.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 14;10(20):4720. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204720. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34682843 Free PMC article.
-
Silicone septal splint for recurrent epistaxis in HHT patients: experience of a national referral centre.Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2023 Apr;43(Suppl. 1):S28-S33. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-suppl.1-43-2023-03. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2023. PMID: 37698097 Free PMC article.
-
HHT-Related Epistaxis and Pregnancy-A Retrospective Survey and Recommendations for Management from an Otorhinolaryngology Perspective.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 13;11(8):2178. doi: 10.3390/jcm11082178. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35456271 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of nasal closure on quality of life in patients with hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2018 Apr 19;3(3):178-181. doi: 10.1002/lio2.157. eCollection 2018 Jun. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2018. PMID: 30062132 Free PMC article.
-
Surgery or No Surgery? Exploring the Dilemma of Epistaxis Management in Patients with HHT.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 15;13(6):1688. doi: 10.3390/jcm13061688. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38541913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braverman IM, Keh A, Jacobson BS. Ultrastructure and three-dimensional organization of the telangiectases of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Invest Dermatol. 1990 Oct;95(4):422–7. - PubMed
-
- Faughnan ME, Palda VA, Garcia-Tsao G, Geisthoff UW, McDonald J, Proctor DD, et al. International guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. J Med Genet. 2011 Feb;48(2):73–87. - PubMed
-
- Byahatti SV, Rebeiz EE, Shapshay SM. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: what the otolaryngologist should know. Am J Rhinol. 1997 Jan-Feb;11(1):55–62. - PubMed
-
- Geisthoff UW, Schneider G, Fischinger J, Plinkert PK. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler’s disease): an interdisciplinary challenge. HNO. 2002 Feb;50(2):114–28. - PubMed
-
- Guttmacher AE, Marchuk DA, White RI Jr. Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. N Engl J Med. 1995 Oct;333(14):918–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

