HIV-1 Vpr Inhibits Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication by Inducing MicroRNA miR-942-5p and Activating NF-κB Signaling
- PMID: 27440900
- PMCID: PMC5021437
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00797-16
HIV-1 Vpr Inhibits Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Lytic Replication by Inducing MicroRNA miR-942-5p and Activating NF-κB Signaling
Abstract
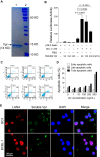
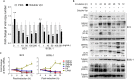
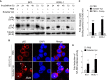
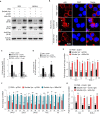
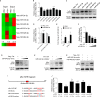
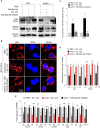
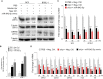
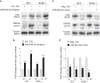
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) infection is required for the development of several AIDS-related malignancies, including Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). The high incidence of AIDS-KS has been ascribed to the interaction of KSHV and HIV-1. We have previously shown that HIV-1-secreted proteins Tat and Nef regulate the KSHV life cycle and synergize with KSHV oncogenes to promote angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Here, we examined the regulation of KSHV latency by HIV-1 viral protein R (Vpr). We found that soluble Vpr inhibits the expression of KSHV lytic transcripts and proteins, as well as viral particle production by activating NF-κB signaling following internalization into PEL cells. By analyzing the expression profiles of microRNAs combined with target search by bioinformatics and luciferase reporter analyses, we identified a Vpr-upregulated cellular microRNA (miRNA), miR-942-5p, that directly targeted IκBα. Suppression of miR-942-5p relieved the expression of IκBα and reduced Vpr inhibition of KSHV lytic replication, while overexpression of miR-942-5p enhanced Vpr inhibition of KSHV lytic replication. Our findings collectively illustrate that, by activating NF-κB signaling through upregulating a cellular miRNA to target IκBα, internalized HIV-1 Vpr inhibits KSHV lytic replication. These results have demonstrated an essential role of Vpr in the life cycle of KSHV.
Importance: Coinfection by HIV-1 promotes the aggressive growth of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)-related malignancies, including Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). In this study, we have shown that soluble HIV-1 Vpr inhibits KSHV lytic replication by activating NF-κB signaling following internalization into PEL cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that a cellular microRNA upregulated by Vpr, miR-942-5p, directly targeted IκBα. Suppression of miR-942-5p relieved IκBα expression and reduced Vpr inhibition of KSHV replication, while overexpression of miR-942-5p enhanced Vpr inhibition of KSHV replication. These results indicate that by activating NF-κB signaling through upregulating a cellular miRNA to target IκBα, internalized Vpr inhibits KSHV lytic replication. This work illustrates a molecular mechanism by which HIV-1-secreted regulatory protein Vpr regulates KSHV latency and the pathogenesis of AIDS-related malignancies.
Copyright © 2016, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Upregulation of MicroRNA 711 Mediates HIV-1 Vpr Promotion of Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Latency and Induction of Pro-proliferation and Pro-survival Cytokines by Targeting the Notch/NF-κB-Signaling Axis.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00580-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00580-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29976660 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic replication by HIV-1 Nef and cellular microRNA hsa-miR-1258.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):4987-5000. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00025-14. Epub 2014 Feb 19. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24554664 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-891a-5p mediates HIV-1 Tat and KSHV Orf-K1 synergistic induction of angiogenesis by activating NF-κB signaling.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 30;43(19):9362-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv988. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26446987 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
[Replication Machinery of Kaposi's Sarcoma-associated Herpesvirus and Drug Discovery Research].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019;139(1):69-73. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.18-00164-2. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2019. PMID: 30606932 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
MiR-942-3p Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Targeting MBL2.Cancer Control. 2019 Jan-Dec;26(1):1073274819846593. doi: 10.1177/1073274819846593. Cancer Control. 2019. PMID: 31046434 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Bacteria in KSHV Infection and KSHV-Induced Cancers.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 25;13(17):4269. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174269. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic and epitranscriptomic regulation during oncogenic γ-herpesvirus infection.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jan 7;15:1484455. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1484455. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39839102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Prominent Role of miR-942 in Carcinogenesis of Tumors.Adv Biomed Res. 2022 Jul 29;11:63. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_226_21. eCollection 2022. Adv Biomed Res. 2022. PMID: 36133499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of glucocorticoid receptor signaling inhibits KSHV-induced inflammation and tumorigenesis.mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0301123. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03011-23. Epub 2023 Dec 20. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38117084 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

