Who Watches the Watchmen: Roles of RNA Modifications in the RNA Interference Pathway
- PMID: 27441695
- PMCID: PMC4956115
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006139
Who Watches the Watchmen: Roles of RNA Modifications in the RNA Interference Pathway
Abstract
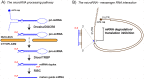
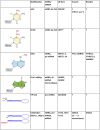
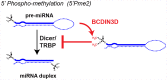
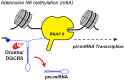
RNA levels are widely thought to be predictive of RNA function. However, the existence of more than a hundred chemically distinct modifications of RNA alone is a major indication that these moieties may impart distinct functions to subgroups of RNA molecules that share a primary sequence but display distinct RNA "epigenetic" marks. RNAs can be modified on many sites, including 5' and 3' ends, the sugar phosphate backbone, or internal bases, which collectively provide many opportunities for posttranscriptional regulation through a variety of mechanisms. Here, we will focus on how modifications on messenger and microRNAs may affect the process of RNA interference in mammalian cells. We believe that taking RNA modifications into account will not only advance our understanding of this crucial pathway in disease and cancer but will also open the path to exploiting the enzymes that "write" and "erase" them as targets for therapeutic drug development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

