Impact of sex disparities on the clinical manifestations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 27442661
- PMCID: PMC5265778
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004272
Impact of sex disparities on the clinical manifestations in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic autoimmune multiorgan disorder of unknown etiology. It affects both men and women, but with different disease manifestations of differing disease severity and in varying proportion, with a female predominance of approximately 90%. There have been numerous studies addressing this issue, especially its implications in relation to optimal sex-tailored treatment and improvement of survival rate; however, further research is warranted. A meta-analysis of studies was performed to compare the impact of sex on the clinical outcomes of SLE in different populations.
Methods: A literature search of the MEDLINE/PubMed and EMBASE databases (until January 2016) was conducted to identify relevant articles. Clinical manifestations reported in these patients were considered as endpoints for this meta-analysis. Two independent reviewers determined eligibility criteria. A fixed-effect model has been used where a small heterogeneity was observed, or else, a random-effect model has been used among the studies. Odd ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) was used to express the pooled effect on dichotomous variables, and the pooled analyses were performed with RevMan 5.3.
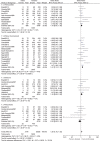
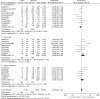
Results: Sixteen studies consisting of a total of 11,934 SLE patients (10,331 females and 1603 males) have been included in this meta-analysis. The average female-to-male ratio of all the included studies is around 9.3:1. Several statistically significant differences were found: alopecia, photosensitivity, and oral ulcers were significantly higher in female patients (OR 0.36, 95% CI 0.29-0.46, P < 0.00001; OR 0.72, 95% CI 0.63-0.83, P < 0.00001; and OR 0.70, 95% CI 0.60-0.82, P < 0.00001, respectively). Malar rash was significantly higher in female patients (OR 0.68, 95% CI 0.53-0.88, P = 0.003), and arthritis was significantly lower in male patients (OR 0.72, 95% CI 1.25-1.84, P < 0.00001). However, serositis and pleurisies were significantly higher in female patients (OR 1.52, 95% CI 1.25-1.84 P < 0.0001; and OR 1.26, 95% CI 1.07-1.48, P = 0.006, respectively). Renal involvement was higher in male patients (OR 1.51, 95% CI 1.31-1.75, P < 0.00001).
Conclusion: The results of this meta-analysis suggest that alopecia, photosensitivity, oral ulcers, arthritis, malar rash, lupus anticoagulant level, and low level of C3 were significantly higher in female lupus patients, whereas renal involvement, serositis and pleurisies, thrombocytopenia, and anti-double stranded deoxyribonucleic acid level were predominant in male patients.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Are anti-nucleosome antibodies a better diagnostic marker than anti-dsDNA antibodies for systemic lupus erythematosus? A systematic review and a study of metanalysis.Autoimmun Rev. 2012 Dec;12(2):97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2012.07.002. Epub 2012 Jul 15. Autoimmun Rev. 2012. PMID: 22810055
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
Cited by
-
The Importance of Sex Stratification in Autoimmune Disease Biomarker Research: A Systematic Review.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1208. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01208. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915581 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative p16 and p21 action protects female astrocytes from transformation.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018 Feb 20;6(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s40478-018-0513-5. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2018. PMID: 29458417 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Quality Measures to Identify Disparities in Health Care for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2020 Nov;46(4):623-638. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2020.07.003. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 32981640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Worse cardiovascular and renal outcome in male SLE patients.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 30;13(1):18628. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45171-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37903784 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis on Sex and Gender in Preparatory Material for National Medical Examination in Germany and the United States.J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020 Jan 10;7:2382120519894253. doi: 10.1177/2382120519894253. eCollection 2020 Jan-Dec. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020. PMID: 32363236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manzi S. Epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Manag Care 2001; 7 (16 Suppl):S474–S479. - PubMed
-
- Stefanidou S, Benos A, Galanopoulou V, et al. Clinical expression and morbidity of systemic lupus erythematosus during a post-diagnostic 5-year follow-up: a male: female comparison. Lupus 2011; 20:1090–1094. - PubMed
-
- Borba EF, Araujo DB, Bonfa E, et al. Clinical and immunological features of 888 Brazilian systemic lupus patients from a monocentric cohort: comparison with other populations. Lupus 2013; 22:744–749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

