Pulmonary Hypertension in Children
- PMID: 27443141
- PMCID: PMC4959130
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccl.2016.04.005
Pulmonary Hypertension in Children
Abstract
The prevalence of PH is increasing in the pediatric population, because of improved recognition and increased survival of patients, and remains a significant cause of morbidity and mortality. Recent studies have improved the understanding of pediatric PH, but management remains challenging because of a lack of evidence-based clinical trials. The growing contribution of developmental lung disease requires dedicated research to explore the use of existing therapies as well as the creation of novel therapies. Adequate study of pediatric PH will require multicenter collaboration due to the small numbers of patients, multifactorial disease causes, and practice variability.
Keywords: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia; Pulmonary arterial hypertension; Single-ventricle circulation.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








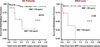




References
-
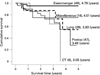
- D'Alonzo GE, Barst RJ, Ayres SM, et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension. Results from a national prospective registry. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115:343–349. - PubMed
-
- Barst RJ, Maislin G, Fishman AP. Vasodilator therapy for primary pulmonary hypertension in children. Circulation. 1999;99:1197–1208. - PubMed
-
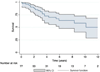
- Zijlstra WM, Douwes JM, Rosenzweig EB, et al. Survival differences in pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension: clues to a better understanding of outcome and optimal treatment strategies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:2159–2169. - PubMed
-
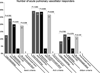
- Ivy DD, Abman SH, Barst RJ, et al. Pediatric pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:D117–D126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

