The first non Clostridial botulinum-like toxin cleaves VAMP within the juxtamembrane domain
- PMID: 27443638
- PMCID: PMC4957215
- DOI: 10.1038/srep30257
The first non Clostridial botulinum-like toxin cleaves VAMP within the juxtamembrane domain
Abstract
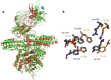
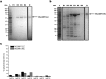
The genome of Weissella oryzae SG25T was recently sequenced and a botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT) like gene was identified by bioinformatics methods. The typical three-domains organization of BoNTs with a N-terminal metalloprotease domain, a translocation and a cell binding domains could be identified. The BoNT family of neurotoxins is rapidly growing, but this was the first indication of the possible expression of a BoNT toxin outside the Clostridium genus. We performed molecular modeling and dynamics simulations showing that the 50 kDa N-terminal domain folds very similarly to the metalloprotease domain of BoNT/B, whilst the binding part is different. However, neither the recombinant metalloprotease nor the binding domains showed cross-reactivity with the standard antisera that define the seven serotypes of BoNTs. We found that the purified Weissella metalloprotease cleaves VAMP at a single site untouched by the other VAMP-specific BoNTs. This site is a unique Trp-Trp peptide bond located within the juxtamembrane segment of VAMP which is essential for neurotransmitter release. Therefore, the present study identifies the first non-Clostridial BoNT-like metalloprotease that cleaves VAMP at a novel and relevant site and we propose to label it BoNT/Wo.
Figures
References
-
- Johnson E. A. & Montecucco C. Botulism. Handb Clin Neurol 91, 333–368 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Hill K. K. & Smith T. J. Genetic diversity within Clostridium botulinum serotypes, botulinum neurotoxin gene clusters and toxin subtypes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 364, 1–20 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, D. o. H. a. H. S. Vol. 77 61083–61115 (Fed. Regist., 2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

