Computational models for predicting drug responses in cancer research
- PMID: 27444372
- PMCID: PMC5862310
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbw065
Computational models for predicting drug responses in cancer research
Abstract
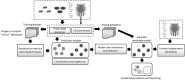
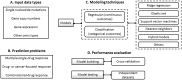
The computational prediction of drug responses based on the analysis of multiple types of genome-wide molecular data is vital for accomplishing the promise of precision medicine in oncology. This will benefit cancer patients by matching their tumor characteristics to the most effective therapy available. As larger and more diverse layers of patient-related data become available, further demands for new bioinformatics approaches and expertise will arise. This article reviews key strategies, resources and techniques for the prediction of drug sensitivity in cell lines and patient-derived samples. It discusses major advances and challenges associated with the different model development steps. This review highlights major trends in this area, and will assist researchers in the assessment of recent progress and in the selection of approaches to emerging applications in oncology.
Keywords: cancer; computational prediction models; drug sensitivity; precision medicine; translational bioinformatics.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Adams JU. Genetics: big hopes for big data. Nature 2015;527(7578):S108–9. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt C. Cancer: reshaping the cancer clinic. Nature 2015;527(7576):S10–1. - PubMed
-
- Rubin MA. Health: make precision medicine work for cancer care. Nature 2015;520(7547):290–1. - PubMed
-
- Kohane IS. Health care policy. Ten things we have to do to achieve precision medicine. Science 2015;349(6243):37–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

