Aptamer-Based Proteomic Profiling Reveals Novel Candidate Biomarkers and Pathways in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 27444932
- PMCID: PMC4963294
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.021803
Aptamer-Based Proteomic Profiling Reveals Novel Candidate Biomarkers and Pathways in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
Background: Single-stranded DNA aptamers are oligonucleotides of ≈50 base pairs in length selected for their ability to bind proteins with high specificity and affinity. Emerging DNA aptamer-based technologies may address limitations of existing proteomic techniques, including low sample throughput, which have hindered proteomic analyses of large cohorts.
Methods: To identify early biomarkers of myocardial injury, we applied an aptamer-based proteomic platform that measures 1129 proteins to a clinically relevant perturbational model of planned myocardial infarction (PMI), patients undergoing septal ablation for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Blood samples were obtained before and at 10 and 60 minutes after PMI, and protein changes were assessed by repeated-measures analysis of variance. The generalizability of our PMI findings was evaluated in a spontaneous myocardial infarction cohort (Wilcoxon rank-sum). We then tested the platform's ability to detect associations between proteins and Framingham Risk Score components in the Framingham Heart Study, performing regression analyses for each protein versus each clinical trait.
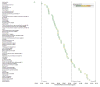
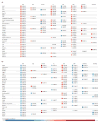
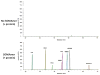
Results: We found 217 proteins that significantly changed in the peripheral vein blood after PMI in a derivation cohort (n=15; P<5.70E-5). Seventy-nine of these proteins were validated in an independent PMI cohort (n=15; P<2.30E-4); >85% were directionally consistent and reached nominal significance. We detected many protein changes that are novel in the context of myocardial injury, including Dickkopf-related protein 4, a WNT pathway inhibitor (peak increase 124%, P=1.29E-15) and cripto, a growth factor important in cardiac development (peak increase 64%, P=1.74E-4). Among the 40 validated proteins that increased within 1 hour after PMI, 23 were also elevated in patients with spontaneous myocardial infarction (n=46; P<0.05). Framingham Heart Study analyses revealed 156 significant protein associations with the Framingham Risk Score (n=899), including aminoacylase 1 (β=0.3386, P=2.54E-22) and trigger factor 2 (β=0.2846, P=5.71E-17). Furthermore, we developed a novel workflow integrating DNA-based immunoaffinity with mass spectrometry to analytically validate aptamer specificity.
Conclusions: Our results highlight an emerging proteomics tool capable of profiling >1000 low-abundance analytes with high sensitivity and high precision, applicable both to well-phenotyped perturbational studies and large human cohorts, as well.
Keywords: aptamer, nucleotides; cardiovascular diseases; mass spectrometry; myocardial infarction; proteomics.
© 2016 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures




Comment in
-
Identifying Low-Abundance Biomarkers: Aptamer-Based Proteomics Potentially Enables More Sensitive Detection in Cardiovascular Diseases.Circulation. 2016 Jul 26;134(4):286-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022940. Circulation. 2016. PMID: 27444931 No abstract available.
-
A Novel Discovery Platform: Aptamers for the Quantification of Human Proteins.Clin Chem. 2017 Jun;63(6):1061-1062. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2016.265652. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Clin Chem. 2017. PMID: 28249843 No abstract available.
References
-
- Keshishian H, Burgess MW, Gillette MA, Mertins P, Clauser KR, Mani DR, Kuhn EW, Farrell LA, Gerszten RE, Carr SA. Multiplexed, quantitative workflow for sensitive biomarker discovery in plasma yields novel candidates for early myocardial injury. Molecular & cellular proteomics: MCP. 2015;14:2375–2393. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Addona TA, Shi X, Keshishian H, Mani DR, Burgess M, Gillette MA, Clauser KR, Shen D, Lewis GD, Farrell LA, Fifer MA, Sabatine MS, Gerszten RE, Carr SA. A pipeline that integrates the discovery and verification of plasma protein biomarkers reveals candidate markers for cardiovascular disease. Nature biotechnology. 2011;29:635–643. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yin X, Subramanian S, Hwang SJ, O’Donnell CJ, Fox CS, Courchesne P, Muntendam P, Gordon N, Adourian A, Juhasz P, Larson MG, Levy D. Protein biomarkers of new-onset cardiovascular disease: Prospective study from the systems approach to biomarker research in cardiovascular disease initiative. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2014;34:939–945. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

