Case Studies Illustrating Focal Alzheimer's, Fluent Aphasia, Late-Onset Memory Loss, and Rapid Dementia
- PMID: 27445249
- PMCID: PMC4958912
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncl.2016.04.008
Case Studies Illustrating Focal Alzheimer's, Fluent Aphasia, Late-Onset Memory Loss, and Rapid Dementia
Abstract
Many dementia subtypes have more shared signs and symptoms than defining ones. We review 8 cases with 4 overlapping syndromes and demonstrate how to distinguish the cases. These include focal cortical presentations of Alzheimer's disease (AD; posterior cortical atrophy and corticobasal syndrome [CBS]), fluent aphasia (semantic dementia and logopenic aphasia), late-onset slowly progressive dementia (hippocampal sclerosis and limbic predominant AD) and rapidly progressive dementia (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and limbic encephalitis). Recognizing the different syndromes can help the clinician to improve their diagnostic skills, leading to improved patient outcomes by early and accurate diagnosis, prompt treatment, and appropriate counseling and guidance.
Keywords: Atypical Alzheimer’s; Fluent aphasia; Late-onset dementia; Rapid dementia.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




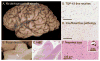
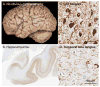


Similar articles
-
Focal cortical presentations of Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2007 Oct;130(Pt 10):2636-45. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm213. Brain. 2007. PMID: 17898010
-
The clinical diagnosis of early-onset dementias: diagnostic accuracy and clinicopathological relationships.Brain. 2011 Sep;134(Pt 9):2478-92. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr189. Epub 2011 Aug 11. Brain. 2011. PMID: 21840888
-
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease presenting as isolated aphasia.Neurology. 1989 Jan;39(1):55-8. doi: 10.1212/wnl.39.1.55. Neurology. 1989. PMID: 2642613
-
[Posterior cortical atrophy--a new dementia syndrome or a form of Alzheimer's disease?].Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 1996 Dec;64(12):492-508. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-996595. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr. 1996. PMID: 9053390 Review. German.
-
[Current concepts regarding cortical dementia].Brain Nerve. 2015 Apr;67(4):389-402. doi: 10.11477/mf.1416200155. Brain Nerve. 2015. PMID: 25846588 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Aug 2;14(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0333-5. Mol Neurodegener. 2019. PMID: 31375134 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Continuity and Stability in Development.Child Dev Perspect. 2017 Jun;11(2):113-119. doi: 10.1111/cdep.12221. Epub 2017 Jan 19. Child Dev Perspect. 2017. PMID: 29503666 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kokmen E, Naessens JM, Offord KP. A short test of mental status: description and preliminary results. Mayo Clin Proc. 1987;62(4):281–8. - PubMed
-
- Benson DF, Davis RJ, Snyder BD. Posterior cortical atrophy. Arch Neurol. 1988;45(7):789–93. - PubMed
-
- Hof PR, et al. Atypical form of Alzheimer’s disease with prominent posterior cortical atrophy: a review of lesion distribution and circuit disconnection in cortical visual pathways. Vision Res. 1997;37(24):3609–25. - PubMed
-
- Tang-Wai DF, et al. Clinical, genetic, and neuropathologic characteristics of posterior cortical atrophy. Neurology. 2004;63(7):1168–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

