Basidiomycete yeasts in the cortex of ascomycete macrolichens
- PMID: 27445309
- PMCID: PMC5793994
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaf8287
Basidiomycete yeasts in the cortex of ascomycete macrolichens
Abstract
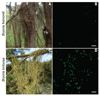
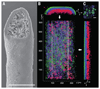
For over 140 years, lichens have been regarded as a symbiosis between a single fungus, usually an ascomycete, and a photosynthesizing partner. Other fungi have long been known to occur as occasional parasites or endophytes, but the one lichen-one fungus paradigm has seldom been questioned. Here we show that many common lichens are composed of the known ascomycete, the photosynthesizing partner, and, unexpectedly, specific basidiomycete yeasts. These yeasts are embedded in the cortex, and their abundance correlates with previously unexplained variations in phenotype. Basidiomycete lineages maintain close associations with specific lichen species over large geographical distances and have been found on six continents. The structurally important lichen cortex, long treated as a zone of differentiated ascomycete cells, appears to consistently contain two unrelated fungi.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures


References
-
- De Bary A. Die Erscheinung der Symbiose. Verlag Karl Trübner; 1879.
-
- Hawksworth DL. The variety of fungal-algal symbioses, their evolutionary significance, and the nature of lichens. Bot J Linn Soc. 1988;96:3–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1095-8339.1988.tb00623.x. - DOI
-
- Ahmadjian V. The Lichen Symbiosis. John Wiley & Sons; 1993.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

