IgG4 Related Lung Disease
- PMID: 27445515
- PMCID: PMC4904546
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/1409281
IgG4 Related Lung Disease
Abstract
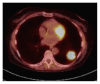
IgG4 related disease is a poorly understood immune mediated condition. Lung involvement is rare and difficult to diagnose and can mimic primary lung malignancy on imaging. A patient who was found to have an incidental lung lesion with risk factors for primary pulmonary malignancy is reported.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical