Antiamoebic Activity of Adenophyllum aurantium (L.) Strother and Its Effect on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 27445810
- PMCID: PMC4922267
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00169
Antiamoebic Activity of Adenophyllum aurantium (L.) Strother and Its Effect on the Actin Cytoskeleton of Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
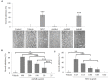
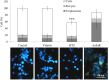
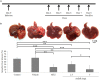
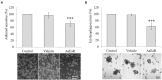
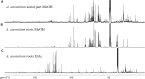
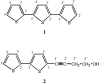
In Mexico, the Adenophyllum aurantium (L.) Strother plant is consumed as an infusion to treat intestinal diseases such as amoebiasis, which is an endemic health problem in Mexico and other countries. However, the effect of A. aurantium on Entamoeba histolytica, the causative agent of amoebiasis, is unknown. An aerial part methanolic extract (AaMeA), a root methanolic extract (AaMeR) and a root ethyl acetate extract (AaEaR) were tested on E. histolytica trophozoites. AaMeA and AaMeR did not show antiproliferative activity; however, AaEaR exhibited an in vitro GI50 of 230 μg/ml, and it was able to inhibit the differentiation of Entamoeba invadens trophozoites into cysts. The intraperitoneal administration of AaEaR (2.5 or 5 mg) to hamsters that were infected with E. histolytica inhibited the development of amoebic liver abscesses in 48.5 or 89.0% of the animals, respectively. Adhesion to fibronectin and erythrophagocytosis were 28.7 and 37.5% inhibited by AaEaR, respectively. An ultrastructure analysis of AaEaR-treated trophozoites shows a decrease in the number of vacuoles but no apparent cell damage. Moreover, this extract affected the actin cytoskeleton structuration, and it prevented the formation of contractile rings by mechanism(s) that were independent of reactive oxygen species and RhoA activation pathways. (13)C NMR data showed that the major compounds in the AaEaR extract are thiophenes. Our results suggest that AaEaR may be effective in treatments against amoebiasis, nevertheless, detailed toxicity studies on thiophenes, contained in AaEaR, are required to avoid misuse of this vegetal species.
Keywords: Adenophyllum aurantium; Entamoeba histolytica; actin; amoebiasis; cytoskeleton; encystation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of jasplakinolide on the growth, encystation, and actin cytoskeleton of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba invadens.J Parasitol. 2001 Apr;87(2):399-405. doi: 10.1645/0022-3395(2001)087[0399:EOJOTG]2.0.CO;2. J Parasitol. 2001. PMID: 11318572
-
Alpha-terthienyl increases filamentous actin of Entamoeba histolytica.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2022 Nov;252:111512. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2022.111512. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 36084901
-
In Vitro Study of Antiamoebic Activity of Methanol Extracts of Argemone mexicana on Trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica HM1-IMSS.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2018 Jul 30;2018:7453787. doi: 10.1155/2018/7453787. eCollection 2018. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30154943 Free PMC article.
-
Public health and clinical importance of amoebiasis in Malaysia: a review.Trop Biomed. 2011 Aug;28(2):194-222. Trop Biomed. 2011. PMID: 22041740 Review.
-
New insights into host-pathogen interactions during Entamoeba histolytica liver infection.Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2011 Mar;1(1):10-8. doi: 10.1556/EuJMI.1.2011.1.4. Eur J Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 2011. PMID: 24466432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Dichloromethane Fraction of Croton sonorae, A Plant Used in Sonoran Traditional Medicine, Affect Entamoeba histolytica Erythrophagocytosis and Gene Expression.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Jul 23;11:693449. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.693449. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34368014 Free PMC article.
-
Entamoeba histolytica: Membrane and Non-Membrane Protein Structure, Function, Immune Response Interaction, and Vaccine Development.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Oct 31;12(11):1079. doi: 10.3390/membranes12111079. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36363634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Stevioside (Stevia rebaudiana) on Entamoeba histolytica Trophozoites.Pathogens. 2024 Apr 30;13(5):373. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13050373. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38787225 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical profile, antimicrobial activity, and leaf anatomy of Adenophyllum porophyllum var. cancellatum.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 11;13:981959. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.981959. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36304152 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids as a Natural Treatment Against Entamoeba histolytica.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018 Jun 22;8:209. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00209. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29988403 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alonso-Castro A. J., Villarreal M. L., Salazar-Olivo L. A., Gomez-Sánchez M., Domínguez F., García-Carranca A. (2011). Mexican medicinal plants used for cancer treatment: pharmacological, phytochemical and ethnobotanical studies. J. Ethnopharmacol. 133 945–972. 10.1016/j.jep.2010.11.055 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ávila-Blanco M. E., Rodríguez M. G., Moreno Duque J. L., Muñoz-Ortega M., Ventura-Juárez J. (2014). Amoebicidal activity of essential oil of Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants in an amoebic liver abscess Hamster model. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014:930208 10.1155/2014/930208 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

