Understanding Dysregulated Behaviors and Compulsions: An Extension of the Emotional Cascade Model and the Mediating Role of Intrusive Thoughts
- PMID: 27445948
- PMCID: PMC4925676
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00994
Understanding Dysregulated Behaviors and Compulsions: An Extension of the Emotional Cascade Model and the Mediating Role of Intrusive Thoughts
Abstract
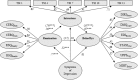
Objective: The Emotional Cascade Model (ECM) by Selby et al. (2008) proposes that people often engage in dysregulated behaviors to end extreme, aversive emotional states triggered by a self-perpetuating vicious cycle of (excessive) rumination, negative affect, and attempts to suppress negative thoughts.
Method: Besides replicating the ECM, we introduced intrusions as a mediator between rumination and behavioral dysregulation and tested this extended ECM for compulsions as part of obsessive-compulsive disorders. A structural equation modeling approach was used to test this in a sample of N = 414, randomly recruited from the general population.
Results: Intrusions were found to fully mediate the effect of rumination on a broad array of dysregulated behaviors and compulsions. This mediation endured when controlling for symptoms of depression.
Conclusion: These findings support the idea that rumination fuels intrusions, which in turn foster dysregulated behaviors. Therefore, addressing rumination as well as intrusions may improve psychotherapeutic interventions for mental disorders characterized by dysregulated behaviors and/or extreme aversive emotional states.
Keywords: (cognitive) emotion regulation; behavioral dysregulation; compulsions; emotional cascades; intrusion.
Figures

References
-
- Abramowitz J. S., Jacoby J. (2015). Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder in Adults. Boston, MA: Hogrefe.
-
- Anestis M. D., Anestis J. C., Selby E. A., Joiner T. E. (2009). Anger rumination across forms of aggression. Pers. Individ. Dif. 46 192–196. 10.1016/j.paid.2008.09.026 - DOI
-
- Backhaus K., Erichson B., Plinke W., Weiber R. (2003). Multivariate Analysemethoden. Eine anwendungsorientierte Einführung (7. Auflage). Berlin: Springer.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

