MyomiRs as Markers of Insulin Resistance and Decreased Myogenesis in Skeletal Muscle of Diet-Induced Obese Mice
- PMID: 27445979
- PMCID: PMC4921801
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2016.00076
MyomiRs as Markers of Insulin Resistance and Decreased Myogenesis in Skeletal Muscle of Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
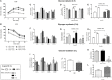
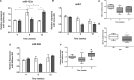
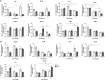
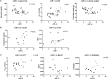
High-fat diet (HFD) feeding causes insulin resistance (IR) in skeletal muscle of mice, which affects skeletal muscle metabolism and function. The involvement of muscle-specific microRNAs in the evolution of skeletal muscle IR during 4, 8, and 12 weeks in HFD-induced obese mice was investigated. After 4 weeks in HFD, mice were obese, hyperglycemic, and hyperinsulinemic; however, their muscles were responsive to insulin stimuli. Expressions of MyomiRs (miR-1, miR-133a, and miR-206) measured in soleus muscles were not different from those found in control mice. After 8 weeks of HFD feeding, glucose uptake was lower in skeletal muscle from obese mice compared to control mice, and we observed a significant decrease in miR-1a in soleus muscle when compared to HFD for 4 weeks. miR-1a expression continued to decay within time. After 12 weeks of HFD, miR-133a expression was upregulated when compared to the control group. Expression of miR-1a was negatively correlated with glycemia and positively correlated with the constant rate of plasma glucose disappearance. Pioglitazone treatment could not reverse decreases of miR-1a levels induced by HFD. Targets of myomiRs involved in insulin-growth factor (IGF)-1 pathway, such as Igf-1, Irs-1, Rheb, and follistatin, were reduced after 12 weeks in HFD and Mtor increased, when compared to the control or HFD for 4 or 8 weeks. These findings suggest for the first time that miR-1 may be a marker of the development of IR in skeletal muscle. Evidence was also presented that impairment in myomiRs expression contributes to decreased myogenesis and skeletal muscle growth reported in diabetes.
Keywords: IGF-1; high-fat diet; insulin resistance; microRNA; myogenesis; myomiRs; skeletal muscle.
Figures


References
-
- Olefsky JM, Nolan JJ. Insulin resistance and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Am J Clin Nutr (1995) 61:980S–6S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

