Effects of Short-Term Warming and Altered Precipitation on Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Grassland of the Tibetan Plateau
- PMID: 27446064
- PMCID: PMC4927576
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01032
Effects of Short-Term Warming and Altered Precipitation on Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Grassland of the Tibetan Plateau
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Effects of Short-Term Warming and Altered Precipitation on Soil Microbial Communities in Alpine Grassland of the Tibetan Plateau.Front Microbiol. 2017 Apr 18;8:667. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00667. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28428783 Free PMC article.
Abstract
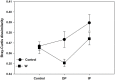
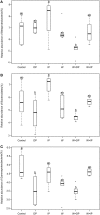
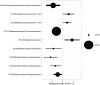
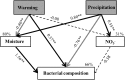
Soil microbial communities are influenced by climate change drivers such as warming and altered precipitation. These changes create abiotic stresses, including desiccation and nutrient limitation, which act on microbes. However, our understanding of the responses of microbial communities to co-occurring climate change drivers is limited. We surveyed soil bacterial and fungal diversity and composition after a 1-year warming and altered precipitation manipulation in the Tibetan plateau alpine grassland. In isolation, warming and decreased precipitation treatments each had no significant effects on soil bacterial community structure; however, in combination of both treatments altered bacterial community structure (p = 0.03). The main effect of altered precipitation specifically impacted the relative abundances of Bacteroidetes and Gammaproteobacteria compared to the control, while the main effect of warming impacted the relative abundance of Betaproteobacteria. In contrast, the fungal community had no significant response to the treatments after 1-year. Using structural equation modeling (SEM), we found bacterial community composition was positively related to soil moisture. Our results indicate that short-term climate change could cause changes in soil bacterial community through taxonomic shifts. Our work provides new insights into immediate soil microbial responses to short-term stressors acting on an ecosystem that is particularly sensitive to global climate change.
Keywords: alpine grassland; climate change; pyrosequencing; soil microbial community structure; soil moisture.
Figures

References
-
- Brzostek E. R., Blair J. M., Dukes J. S., Frey S. D., Hobbie S. E., Melillo J. M., et al. (2012). The effect of experimental warming and precipitation change on proteolytic enzyme activity: positive feedbacks to nitrogen availability are not universal. Glob. Change Biol. 18, 2617–2625. 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2012.02685.x - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

