Guardian of the Human Genome: Host Defense Mechanisms against LINE-1 Retrotransposition
- PMID: 27446907
- PMCID: PMC4924340
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2016.00028
Guardian of the Human Genome: Host Defense Mechanisms against LINE-1 Retrotransposition
Abstract
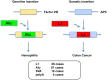
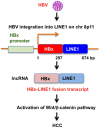
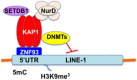
Long interspersed element type 1 (LINE-1, L1) is a mobile genetic element comprising about 17% of the human genome, encoding a newly identified ORF0 with unknown function, ORF1p with RNA-binding activity and ORF2p with endonuclease and reverse transcriptase activities required for L1 retrotransposition. L1 utilizes an endonuclease (EN) to insert L1 cDNA into target DNA, which induces DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) is activated by DSBs and subsequently the ATM-signaling pathway plays a role in regulating L1 retrotransposition. In addition, the host DNA repair machinery such as non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair pathway is also involved in L1 retrotransposition. On the other hand, L1 is an insertional mutagenic agent, which contributes to genetic change, genomic instability, and tumorigenesis. Indeed, high-throughput sequencing-based approaches identified numerous tumor-specific somatic L1 insertions in variety of cancers, such as colon cancer, breast cancer, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). In fact, L1 retrotransposition seems to be a potential factor to reduce the tumor suppressive property in HCC. Furthermore, recent study demonstrated that a specific viral-human chimeric transcript, HBx-L1, contributes to hepatitis B virus (HBV)-associated HCC. In contrast, host cells have evolved several defense mechanisms protecting cells against retrotransposition including epigenetic regulation through DNA methylation and host defense factors, such as APOBEC3, MOV10, and SAMHD1, which restrict L1 mobility as a guardian of the human genome. In this review, I focus on somatic L1 insertions into the human genome in cancers and host defense mechanisms against deleterious L1 insertions.
Keywords: DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs); DNA repair; HBV; LINE-1; epigenetic regulation; retrotransposition; somatic insertion; tumor suppressor.
Figures
References
-
- Armanios M., Chen J. L., Chang Y. P., Brodsky R. A., Hawkins A., Griffin C. A., et al. (2005). Haploinsufficiency of telomerase reverse transcriptase leads to anticipation in autosomal dominant dyskeratosis congenital. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 15960–15964. 10.1073/pnas.0508124102 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

