Secretion of Rhoptry and Dense Granule Effector Proteins by Nonreplicating Toxoplasma gondii Uracil Auxotrophs Controls the Development of Antitumor Immunity
- PMID: 27447180
- PMCID: PMC4957766
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006189
Secretion of Rhoptry and Dense Granule Effector Proteins by Nonreplicating Toxoplasma gondii Uracil Auxotrophs Controls the Development of Antitumor Immunity
Abstract
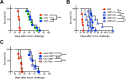
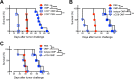
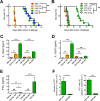
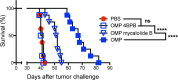
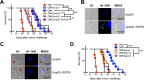
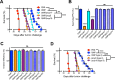
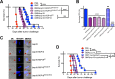
Nonreplicating type I uracil auxotrophic mutants of Toxoplasma gondii possess a potent ability to activate therapeutic immunity to established solid tumors by reversing immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Here we engineered targeted deletions of parasite secreted effector proteins using a genetically tractable Δku80 vaccine strain to show that the secretion of specific rhoptry (ROP) and dense granule (GRA) proteins by uracil auxotrophic mutants of T. gondii in conjunction with host cell invasion activates antitumor immunity through host responses involving CD8α+ dendritic cells, the IL-12/interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) TH1 axis, as well as CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Deletion of parasitophorous vacuole membrane (PVM) associated proteins ROP5, ROP17, ROP18, ROP35 or ROP38, intravacuolar network associated dense granule proteins GRA2 or GRA12, and GRA24 which traffics past the PVM to the host cell nucleus severely abrogated the antitumor response. In contrast, deletion of other secreted effector molecules such as GRA15, GRA16, or ROP16 that manipulate host cell signaling and transcriptional pathways, or deletion of PVM associated ROP21 or GRA3 molecules did not affect the antitumor activity. Association of ROP18 with the PVM was found to be essential for the development of the antitumor responses. Surprisingly, the ROP18 kinase activity required for resistance to IFN-γ activated host innate immunity related GTPases and virulence was not essential for the antitumor response. These data show that PVM functions of parasite secreted effector molecules, including ROP18, manipulate host cell responses through ROP18 kinase virulence independent mechanisms to activate potent antitumor responses. Our results demonstrate that PVM associated rhoptry effector proteins secreted prior to host cell invasion and dense granule effector proteins localized to the intravacuolar network and host nucleus that are secreted after host cell invasion coordinately control the development of host immune responses that provide effective antitumor immunity against established ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma gondii Parasitophorous Vacuole Membrane-Associated Dense Granule Proteins Orchestrate Chronic Infection and GRA12 Underpins Resistance to Host Gamma Interferon.mBio. 2019 Jul 2;10(4):e00589-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00589-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31266861 Free PMC article.
-
Rhoptry and Dense Granule Secreted Effectors Regulate CD8+ T Cell Recognition of Toxoplasma gondii Infected Host Cells.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 6;10:2104. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02104. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31555296 Free PMC article.
-
The Toxoplasma gondii Rhoptry Kinome Is Essential for Chronic Infection.mBio. 2016 May 10;7(3):e00193-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00193-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27165797 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting tumors with nonreplicating Toxoplasma gondii uracil auxotroph vaccines.Trends Parasitol. 2013 Sep;29(9):431-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2013.07.001. Epub 2013 Aug 5. Trends Parasitol. 2013. PMID: 23928100 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii manipulates host cell signaling pathways via its secreted effector molecules.Parasitol Int. 2021 Aug;83:102368. doi: 10.1016/j.parint.2021.102368. Epub 2021 Apr 24. Parasitol Int. 2021. PMID: 33905814 Review.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii Parasitophorous Vacuole Membrane-Associated Dense Granule Proteins Orchestrate Chronic Infection and GRA12 Underpins Resistance to Host Gamma Interferon.mBio. 2019 Jul 2;10(4):e00589-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00589-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31266861 Free PMC article.
-
Synergy between Toxoplasma gondii type I ΔGRA17 immunotherapy and PD-L1 checkpoint inhibition triggers the regression of targeted and distal tumors.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Nov;9(11):e002970. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002970. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34725213 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Sequencing Investigated the Tumor-Related Factors Changes After T. gondii Infection.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 7;10:181. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00181. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30792708 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii profilin and tachyzoites RH strain may manipulate autophagy via downregulating Atg5 and Atg12 and upregulating Atg7.Mol Biol Rep. 2021 Oct;48(10):7041-7047. doi: 10.1007/s11033-021-06667-5. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34453672
-
From pathogen to cure: exploring the antitumor potential of Toxoplasma gondii.Infect Agent Cancer. 2025 Jun 18;20(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13027-025-00673-z. Infect Agent Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40533757 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

