Angiotensin A/Alamandine/MrgD Axis: Another Clue to Understanding Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
- PMID: 27447621
- PMCID: PMC4964474
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms17071098
Angiotensin A/Alamandine/MrgD Axis: Another Clue to Understanding Cardiovascular Pathophysiology
Abstract
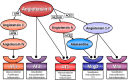
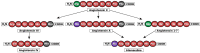
The renin-angiotensin system (RAS) plays a crucial role in cardiovascular regulations and its modulation is a challenging target for the vast majority of cardioprotective strategies. However, many biological effects of these drugs cannot be explained by the known mode of action. Our comprehension of the RAS is thus far from complete. The RAS represents an ingenious system of "checks and balances". It incorporates vasoconstrictive, pro-proliferative, and pro-inflammatory compounds on one hand and molecules with opposing action on the other hand. The list of these molecules is still not definitive because new biological properties can be achieved by minor alteration of the molecular structure. The angiotensin A/alamandine-MrgD cascade associates the deleterious and protective branches of the RAS. Its identification provided a novel clue to the understanding of the RAS. Angiotensin A (Ang A) is positioned at the "crossroad" in this system since it either elicits direct vasoconstrictive and pro-proliferative actions or it is further metabolized to alamandine, triggering opposing effects. Alamandine, the central molecule of this cascade, can be generated both from the "deleterious" Ang A as well as from the "protective" angiotensin 1-7. This pathway modulates peripheral and central blood pressure regulation and cardiovascular remodeling. Further research will elucidate its interactions in cardiovascular pathophysiology and its possible therapeutic implications.
Keywords: MrgD receptor; alamandine; angiotensin A; renin-angiotensin system.
Figures
References
-
- Simko F., Pechanova O., Repova Bednarova K., Krajcirovicova K., Celec P., Kamodyova N., Zorad S., Kucharska J., Gvozdjakova A., Adamcova M., et al. Hypertension and cardiovascular remodelling in rats exposed to continuous light: Protection by ACE-inhibition and melatonin. Mediators Inflamm. 2014 doi: 10.1155/2014/703175. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simko F., Pechanova O., Pelouch V., Krajcirovicova K., Mullerova M., Bednarova K., Adamcova M., Paulis L. Effect of melatonin, captopril, spironolactone and simvastatin on blood pressure and left ventricular remodelling in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 2009;27:S5–S10. doi: 10.1097/01.hjh.0000358830.95439.e8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

