PIM kinases as therapeutic targets against advanced melanoma
- PMID: 27448973
- PMCID: PMC5342389
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10703
PIM kinases as therapeutic targets against advanced melanoma
Abstract
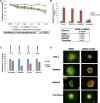
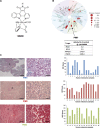
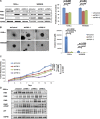
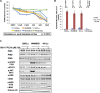
Therapeutic strategies for the treatment of metastatic melanoma show encouraging results in the clinic; however, not all patients respond equally and tumor resistance still poses a challenge. To identify novel therapeutic targets for melanoma, we screened a panel of structurally diverse organometallic inhibitors against human-derived normal and melanoma cells. We observed that a compound that targets PIM kinases (a family of Ser/Thr kinases) preferentially inhibited melanoma cell proliferation, invasion, and viability in adherent and three-dimensional (3D) melanoma models. Assessment of tumor tissue from melanoma patients showed that PIM kinases are expressed in pre- and post-treatment tumors, suggesting PIM kinases as promising targets in the clinic. Using knockdown studies, we showed that PIM1 contributes to melanoma cell proliferation and tumor growth in vivo; however, the presence of PIM2 and PIM3 could also influence the outcome. The inhibition of all PIM isoforms using SGI-1776 (a clinically-available PIM inhibitor) reduced melanoma proliferation and survival in preclinical models of melanoma. This was potentiated in the presence of the BRAF inhibitor PLX4720 and in the presence of PI3K inhibitors. Our findings suggest that PIM inhibitors provide promising additions to the targeted therapies available to melanoma patients.
Keywords: PIM kinases; SGI-1776; melanoma; organometallics; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
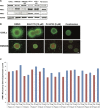
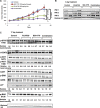

References
-
- Villanueva J, Infante JR, Krepler C, Reyes-Uribe P, Samanta M, Chen HY, Li B, Swoboda RK, Wilson M, Vultur A, Fukunaba-Kalabis M, Wubbenhorst B, Chen TY, et al. Concurrent MEK2 Mutation and BRAF Amplification Confer Resistance to BRAF and MEK Inhibitors in Melanoma. Cell Rep. 2013;4:1090–1099. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, Somasundaram R, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Cipolla AK, Wubbenhorst B, Xu X, Gimotty PA, Kee D, Santiago-Walker AE, Letrero R, D'Andrea K, et al. Acquired Resistance to BRAF Inhibitors Mediated by a RAF Kinase Switch in Melanoma Can Be Overcome by Cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:683–695. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

