Modulation of Circadian Gene Expression and Metabolic Compensation by the RCO-1 Corepressor of Neurospora crassa
- PMID: 27449058
- PMCID: PMC5012383
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.116.191064
Modulation of Circadian Gene Expression and Metabolic Compensation by the RCO-1 Corepressor of Neurospora crassa
Abstract
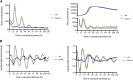
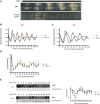
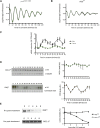
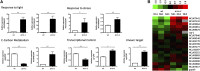
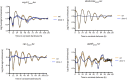
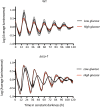
Neurospora crassa is a model organism for the study of circadian clocks, molecular machineries that confer ∼24-hr rhythms to different processes at the cellular and organismal levels. The FREQUENCY (FRQ) protein is a central component of the Neurospora core clock, a transcription/translation negative feedback loop that controls genome-wide rhythmic gene expression. A genetic screen aimed at determining new components involved in the latter process identified regulation of conidiation 1 (rco-1), the ortholog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Tup1 corepressor, as affecting period length. By employing bioluminescent transcriptional and translational fusion reporters, we evaluated frq and FRQ expression levels in the rco-1 mutant background observing that, in contrast to prior reports, frq and FRQ expression are robustly rhythmic in the absence of RCO-1, although both amplitude and period length of the core clock are affected. Moreover, we detected a defect in metabolic compensation, such that high-glucose concentrations in the medium result in a significant decrease in period when RCO-1 is absent. Proteins physically interacting with RCO-1 were identified through co-immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry; these include several components involved in chromatin remodeling and transcription, some of which, when absent, lead to a slight change in period. In the aggregate, these results indicate a dual role for RCO-1: although it is not essential for core-clock function, it regulates proper period and amplitude of core-clock dynamics and is also required for the rhythmic regulation of several clock-controlled genes.
Keywords: Neurospora crassa; circadian clocks; core-clock mechanism; corepressor; frequency.
Copyright © 2016 by the Genetics Society of America.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of WC-independent frequency transcription by RCO-1 is essential for Neurospora circadian clock.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Dec 10;110(50):E4867-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1315133110. Epub 2013 Nov 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 24277852 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation, disorder, and phase separation govern the behavior of Frequency in the fungal circadian clock.Elife. 2024 Mar 25;12:RP90259. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90259. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38526948 Free PMC article.
-
Role for Protein Kinase A in the Neurospora Circadian Clock by Regulating White Collar-Independent frequency Transcription through Phosphorylation of RCM-1.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Jun;35(12):2088-102. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00709-14. Epub 2015 Apr 6. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25848091 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic and Posttranslational Modifications in Light Signal Transduction and the Circadian Clock in Neurospora crassa.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Jul 7;16(7):15347-83. doi: 10.3390/ijms160715347. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26198228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting the mechanisms of the clock in Neurospora.Methods Enzymol. 2015;551:29-52. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2014.10.009. Epub 2014 Dec 26. Methods Enzymol. 2015. PMID: 25662450 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circadian regulation of metabolism across photosynthetic organisms.Plant J. 2023 Nov;116(3):650-668. doi: 10.1111/tpj.16405. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Plant J. 2023. PMID: 37531328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circadian Proteomic Analysis Uncovers Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation in Metabolic Pathways.Cell Syst. 2018 Dec 26;7(6):613-626.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2018.10.014. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Cell Syst. 2018. PMID: 30553726 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian oscillations in Trichoderma atroviride and the role of core clock components in secondary metabolism, development, and mycoparasitism against the phytopathogen Botrytis cinerea.Elife. 2022 Aug 11;11:e71358. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71358. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35950750 Free PMC article.
-
The Third International Symposium on Fungal Stress - ISFUS.Fungal Biol. 2020 May;124(5):235-252. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2020.02.007. Epub 2020 Feb 24. Fungal Biol. 2020. PMID: 32389286 Free PMC article.
-
Methylxanthines Modulate Circadian Period Length Independently of the Action of Phosphodiesterase.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0372722. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03727-22. Epub 2023 Jun 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37272789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aronson B. D., Johnson K. A., Loros J. J., Dunlap J. C., 1994. Negative feedback defining a circadian clock: autoregulation of the clock gene frequency. Science 263: 1578–1584. - PubMed
-
- Bardiya N., Shiu P. K., 2007. Cyclosporin A-resistance based gene placement system for Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet. Biol. 44: 307–314. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

