Neonatal death: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data
- PMID: 27449077
- PMCID: PMC5139812
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.03.040
Neonatal death: Case definition & guidelines for data collection, analysis, and presentation of immunization safety data
Abstract
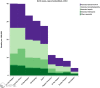
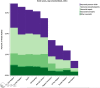
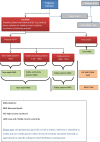
More than 40% of all deaths in children under 5 years of age occur during the neonatal period: the first month of life. Immunization of pregnant women has proven beneficial to both mother and infant by decreasing morbidity and mortality. With an increasing number of immunization trials being conducted in pregnant women, as well as roll-out of recommended vaccines to pregnant women, there is a need to clarify details of a neonatal death. This manuscript defines levels of certainty of a neonatal death, related to the viability of the neonate, who confirmed the death, and the timing of the death during the neonatal period and in relation to immunization of the mother.
Keywords: Adverse event; Case definition; Guidelines; Maternal immunization; Neonatal death.
Copyright © 2016. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Libr.; 2006. Neonatal and perinatal mortality: country, regional and global estimates.
-
- UNICEF, WHO, The World Bank, UN; New York, USA: 2014. Levels and trends in child mortality. Report.
-
- Lawn J.E., Blencowe H., Oza S., You D., Lee A.C.C., Waiswa P. Every newborn: progress, priorities, and potential beyond survival. Lancet. 2014:189–205. - PubMed
-
- Zaman K., Roy E., Arifeen S.E., Rahman M., Raqib R., Wilson E. Effectiveness of maternal influenza immunization in mothers and infants. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(15):1555–1564. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

