A nomogram composed of clinicopathologic features and preoperative serum tumor markers to predict lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer patients
- PMID: 27449100
- PMCID: PMC5312336
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.10732
A nomogram composed of clinicopathologic features and preoperative serum tumor markers to predict lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer patients
Abstract
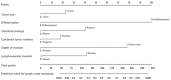
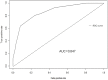
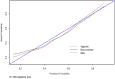
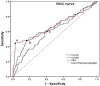
Predicting lymph node metastasis (LNM) accurately is of great importance to formulate optimal treatment strategies preoperatively for patients with early gastric cancer (EGC). This study aimed to explore risk factors that predict the presence of LNM in EGC. A total of 697 patients underwent gastrectomy enrolled in this study, were divided into training and validation set, and the relationship between LNM and other clinicopathologic features, preoperative serum combined tumor markers (CEA, CA19-9, CA125) were evaluated. Risk factors for LNM were identified using logistic regression analysis, and a nomogram was created by R program to predict the possibility of LNM in training set, while receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was applied to assess the predictive value of the nomogram model in validation set. Consequently, LNM was significantly associated with tumor size, macroscopic type, differentiation type, ulcerative findings, lymphovascular invasion, depth of invasion and combined tumor marker. In multivariate logistic regression analysis, factors including of tumor size, differentiation type, ulcerative findings, lymphovascular invasion, depth of invasion and combined tumor marker were demonstrated to be independent risk factors for LNM. Moreover, a predictive nomogram with these independent factors for LNM in EGC patients was constructed, and ROC curve demonstrated a good discrimination ability with the AUC of 0.847 (95% CI: 0.789-0.923), which was significantly larger than those produced in previous studies. Therefore, including of these tumor markers which could be convenient and feasible to obtain from the serum preoperatively, the nomogram could effectively predict the incidence of LNM for EGC patients.
Keywords: early gastric cancer; lymph node metastasis; nomogram; prediction; tumor markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ, He J. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. - PubMed
-
- Saragoni L, Morgagni P, Gardini A, Marfisi C, Vittimberga G, Garcea D, Scarpi E. Early gastric cancer: diagnosis, staging, and clinical impact. Evaluation of 530 patients. New elements for an updated definition and classification. Gastric Cancer. 2013;16:549–554. - PubMed
-
- Yanai H, Matsumoto Y, Harada T, Nishiaki M, Tokiyama H, Shigemitsu T, Tada M, Okita K. Endoscopic ultrasonography and endoscopy for staging depth of invasion in early gastric cancer: a pilot study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;46:212–216. - PubMed
-
- Chung IK, Lee JH, Lee SH, Kim SJ, Cho JY, Cho WY, Hwangbo Y, Keum BR, Park JJ, Chun HJ, Kim HJ, Kim JJ, Ji SR, Seol SY. Therapeutic outcomes in 1000 cases of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: Korean ESD Study Group multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009;69:1228–1235. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

