Five-minute Apgar score ≤ 5 and Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation (MIH) - a case control study
- PMID: 27449152
- PMCID: PMC4957350
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-016-0253-5
Five-minute Apgar score ≤ 5 and Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation (MIH) - a case control study
Abstract
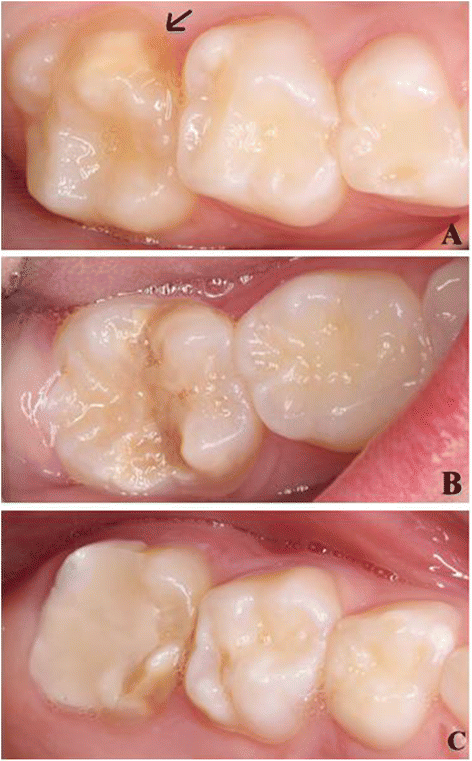
Background: The aetiology of molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH) is unclear. The asymmetric distribution of MIH in the dentition may indicate that an insult of short duration that affects ameloblasts at a vulnerable stage could be a causative factor. Apgar ≤ 5 at 5 min may indicate asphyxia (hypoxic-ischemic insult) during birth. It was hypnotised that low Apgar score during birth may cause MIH. The present study aimed to examine a possible association between Apgar ≤ 5 at 5 min and the occurrence of MIH.
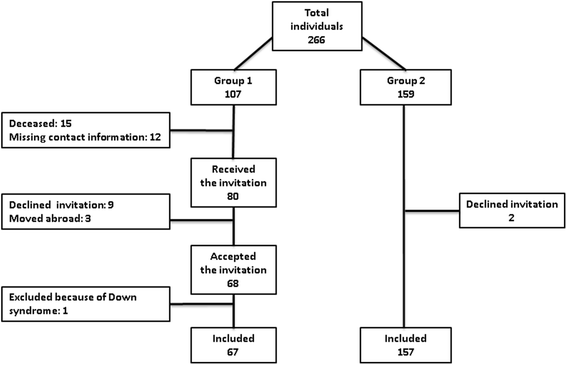
Method: Two study groups were selected for examination. The cases comprised 67 children aged 8-10 years born with Apgar score equal to or below 5 after 5 min. The control group comprised 157 age-matched healthy children. First permanent molars, second primary molars and all permanent incisors were examined in all children. Clinical examination was undertaken by two calibrated examiners and intraoral close-up photographs of the teeth were later evaluated by three calibrated and blinded clinicians. Demarcated opacities, post-eruptive breakdown, atypical restorations and extractions due to MIH, according to the criteria of the European Association of Paediatric Dentistry, were assessed.
Results: The prevalence of MIH did not differ between the two groups. A chi-square test failed to confirm any statistically significant relationship between 5-min Apgar scores and MIH occurrence. In addition, there was no statistically significant relationship between the number of affected first permanent molars in cases and controls.
Conclusion: There was no association between Apgar ≤ 5 at 5 min and the occurrence of MIH.
Keywords: Ameloblasts; Apgar score; Asphyxia; Enamel; Molar incisor hypomineralisation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Best clinical practice guidance for clinicians dealing with children presenting with molar-incisor-hypomineralisation (MIH): an updated European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry policy document.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022 Feb;23(1):3-21. doi: 10.1007/s40368-021-00668-5. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 34669177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molar incisor hypomineralisation and dental caries among children in Slovenia.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2013 Sep;14(3):241-5. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2013. PMID: 24295012
-
Prevalence and aetiology of Molar-Incisor Hypomineralisation among children aged 8-10 years in Tirana, Albania.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2016 Mar;17(1):75-9. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2016. PMID: 26949245
-
Molar-incisor hypomineralisation: prevalence and defect characteristics in Iraqi children.Int J Paediatr Dent. 2011 Nov;21(6):413-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-263X.2011.01143.x. Epub 2011 Jun 20. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2011. PMID: 21689174
-
Molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH).Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2003 Sep;4(3):114-20. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2003. PMID: 14529330 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic profiling of human dental enamel affected by molar incisor hypomineralisation of different clinical severity grades: an in vitro study.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2024 Aug;25(4):533-545. doi: 10.1007/s40368-024-00911-9. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2024. PMID: 38842758 Free PMC article.
-
Is there a rise of prevalence for Molar Incisor Hypomineralization? A meta-analysis of published data.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jan 25;24(1):127. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03637-0. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38273324 Free PMC article.
-
Best clinical practice guidance for clinicians dealing with children presenting with molar-incisor-hypomineralisation (MIH): an updated European Academy of Paediatric Dentistry policy document.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022 Feb;23(1):3-21. doi: 10.1007/s40368-021-00668-5. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 34669177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlation of the Apgar Score with Dental Caries in 3- to 5-year-old Iranian Children.Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024 Apr 24;38:46. doi: 10.47176/mjiri.38.46. eCollection 2024. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 2024. PMID: 39399595 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal vitamin D status in pregnancy and molar incisor hypomineralisation and hypomineralised second primary molars in the offspring at 7-9 years of age: a longitudinal study.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022 Aug;23(4):557-566. doi: 10.1007/s40368-022-00712-y. Epub 2022 May 12. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35553398 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Weerheijm KL, Duggal M, Mejare I, Papagiannoulis L, Koch G, Martens LC, Hallonsten AL. Judgement criteria for molar incisor hypomineralisation (MIH) in epidemiologic studies: a summary of the European meeting on MIH held in Athens, 2003. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2003;4(3):110–113. - PubMed
-
- Simmer JP, Hu JC. Dental enamel formation and its impact on clinical dentistry. J Dent Educ. 2001;65(9):896–905. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

