Kunxian capsules in the treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 27449221
- PMCID: PMC4957347
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1438-6
Kunxian capsules in the treatment of patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease. Kunxian capsule, a Chinese patent medicine which has been used in the treatment of immunologic diseases for many years in China, has anti-inflammatory and immunoregulatory effects. This study investigates the efficacy and safety of Kunxian capsules in the treatment of AS.
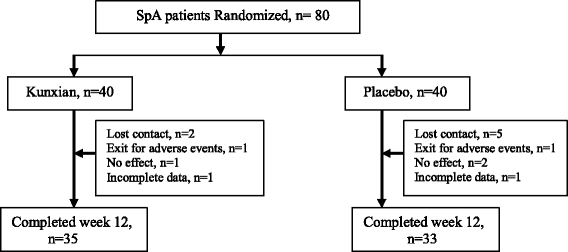
Method: This was a randomized, double-blind, parallel control clinical trial involving 80 patients with AS who fulfilled the modified New York criteria (1984) and had active disease defined by a Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥40 mm under background stable nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for more than 4 weeks. Patients were randomly divided into two groups, the Kunxian group and the placebo group, and Kunxian (0.6 g, three times per day) and the placebo were provided for 12 weeks. The primary endpoint was the Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society (ASAS) 20 response rate at week 12. The secondary endpoints were ASAS 40, BASDAI 50, the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI), Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Metrology Index (BASMI), and Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score on the basis of C-reactive protein level (ASDAS-CRP) at weeks 2, 6, and 12.
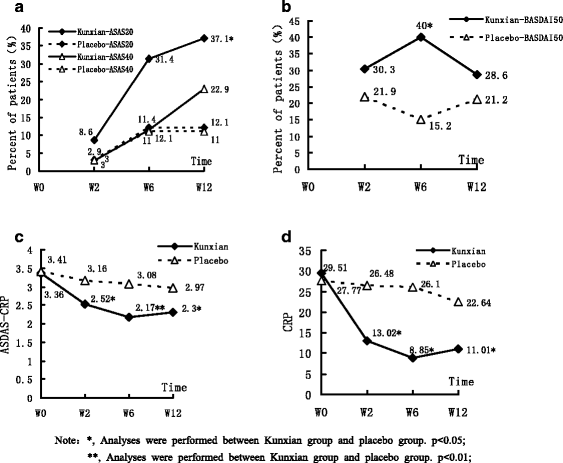
Results: The primary endpoint of ASAS 20 at week 12 was achieved in 13 of 35 patients (37.1 %) among the Kunxian group, compared with 4 of 33 (12.1 %) in the placebo group (p < 0.05). Significant improvement (BASDAI 50) was also observed between the Kunxian group and the placebo group at week 6 (14 (40 %) and 5 (15.5 %), respectively, p < 0.05). At weeks 2, 6, and 12, the ASDAS-CRP level of the Kunxian group was significantly lower than that of the placebo group, especially at week 6 (p < 0.01). Kunxian obviously reduced CRP levels compared to placebo at weeks 2, 6, and 12 (p < 0.05). Compared with the placebo, Kunxian was associated with greater improvements in signs and symptoms of patients with AS from the baseline to week 12, and significant intergroup differences of additional composite indices of disease activity (i.e., erythrocyte sedimentation rate, patient global assessment of disease activity, total back pain, level of morning stiffness, tender joints, and BASFI scores) were also observed.
Conclusion: Kunxian capsule significantly decreased the disease activity of patients with AS.
Trial registration: NCT00953979 . Registered on 5 August 2009.
Keywords: Ankylosing spondylitis; Efficacy; Kunxian capsule; Safety.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of Fengshi Gutong Capsule in patients with active ankylosing spondylitis: A 4-week randomized controlled, double-blinded, double-dummy trial.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Mar 1;285:114731. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114731. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34634368 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of ultrasound treatment applied with exercise therapy on patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.Rheumatol Int. 2016 May;36(5):653-61. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3441-3. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 26923690 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (ASSERT).Arthritis Rheum. 2005 Feb;52(2):582-91. doi: 10.1002/art.20852. Arthritis Rheum. 2005. PMID: 15692973 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Wenbu Zhibi Granule in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov 25;2021:8683600. doi: 10.1155/2021/8683600. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34868333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upadacitinib for axial spondyloarthritis: a meta-analysis of efficacy and safety.Clin Rheumatol. 2024 Aug;43(8):2391-2402. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-07027-x. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Clin Rheumatol. 2024. PMID: 38874670
Cited by
-
Dissecting the Underlying Pharmaceutical Mechanism of Chinese Traditional Medicine Yun-Pi-Yi-Shen-Tong-Du-Tang Acting on Ankylosing Spondylitis through Systems Biology Approaches.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 18;7(1):13436. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13723-3. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29044146 Free PMC article.
-
Network Pharmacology-Based Analysis on the Curative Effect of Kunxian Capsules against Rheumatoid Arthritis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Sep 29;2021:6812374. doi: 10.1155/2021/6812374. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34630616 Free PMC article.
-
Kunxian capsule alleviates podocyte injury and proteinuria by inactivating β-catenin in db/db mice.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 30;10:1213191. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1213191. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37457567 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical study, network pharmacology, and molecular docking of Kunxian capsule in treating idiopathic membranous nephropathy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 6;12:1506972. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1506972. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 39981089 Free PMC article.
-
Successful treatment of synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis and paradoxical skin lesions by Tripterygium wilfordii hook f: a case report.J Int Med Res. 2020 Sep;48(9):300060520949100. doi: 10.1177/0300060520949100. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32962502 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tu L, Rai JC, Cao S, et al. Costs and work limitation of patients with ankylosing spondylitis in China. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32(5):661–6. - PubMed
-
- Zongyu W, Lunhui L. Chinese raw materials botanicals. China, Yunnan. Yunnan Science and Technology Press. 2002;203:333.
-
- Yaofeng H, Xuesong S, Shengjiu G, et al. Analysis on Similarity of Chemical Compositions of between Tripterygium wilfordii Hook.f. and Tripterygium hypoglaucum(Levl) Hutchins. J Anhui AgriSci. 2009;37(13):5961–3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

