Early steatohepatitis in hyperlipidemic mice with endothelial-specific gain of TRPC3 function precedes changes in aortic atherosclerosis
- PMID: 27449657
- PMCID: PMC5005460
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00067.2016
Early steatohepatitis in hyperlipidemic mice with endothelial-specific gain of TRPC3 function precedes changes in aortic atherosclerosis
Abstract
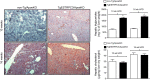
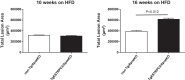
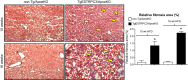
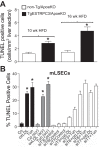
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and its more advanced form nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) are the most common chronic liver diseases in developed countries. Moreover, NAFLD and NASH are considerable risk factors for atherosclerosis, the most frequent vascular pathology in these and other metabolic diseases. Despite this strong connection, current knowledge of the relationship between NAFLD/NASH and atherosclerosis is scarce. Recently, we studied hyperlipidemic Apoe knockout mice with endothelial-specific gain of transient receptor potential canonical 3 channel function (TgESTRPC3/ApoeKO) and found that these animals had increased burden of advanced aortic atherosclerosis (16 wk on high-fat diet) compared with nontransgenic ApoeKO littermate controls (non-Tg/ApoeKO), whereas early lesions (10 wk on high-fat diet) were not different. Here, we report that at the early stage when differences in aortic atherosclerosis are not yet manifest, the livers of TgESTRPC3/ApoeKO mice show steatosis, fibrosis, and altered hepatic enzymes compared with non-Tg/ApoeKO animals. Because differences in liver pathology were noticeable long before differences in atherosclerosis were evident, our studies suggest that TRPC3-related endothelial mechanisms that promote steatohepatitis may also contribute to atherosclerosis progression. In vitro, downregulation of TRPC3 in liver sinusoid endothelial cells reduces their susceptibility to endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis, suggesting that a proapoptotic effect of TRPC3 may add to other fibrogenic factors in vivo. These novel findings show a positive association between augmented expression of an endothelial TRPC channel, development of early steatohepatitis, and atherosclerotic burden in a hyperlipidemic mouse model of NAFLD fed conventional Western-type diet.
Keywords: NAFLD; NASH; TRPC channels; atherosclerosis; endothelium.
Copyright © 2016 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Progression of non-alcoholic steatosis to steatohepatitis and fibrosis parallels cumulative accumulation of danger signals that promote inflammation and liver tumors in a high fat-cholesterol-sugar diet model in mice.J Transl Med. 2015 Jun 16;13:193. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0552-7. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26077675 Free PMC article.
-
Increased size and cellularity of advanced atherosclerotic lesions in mice with endothelial overexpression of the human TRPC3 channel.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 28;112(17):E2201-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1505410112. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25870279 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of TRPC3 or TRPC6 Fails to Attenuate the Formation of Inflammation and Fibrosis in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis.Biol Pharm Bull. 2021;44(3):431-436. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b20-00903. Biol Pharm Bull. 2021. PMID: 33642551
-
[Mechanism Analysis and Prevention of Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis].Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2015;70(3):197-204. doi: 10.1265/jjh.70.197. Nihon Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26411937 Review. Japanese.
-
Utilization of animal models to investigate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 5;7(27):42762-42776. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8641. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27072576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TRPC and TRPV Channels' Role in Vascular Remodeling and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 25;21(17):6125. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176125. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32854408 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Ca2+ channels in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and their implications for therapeutic strategies (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2022 Sep;50(3):113. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2022.5169. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Int J Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35796003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Endothelial Cell Calcium Signaling.Compr Physiol. 2019 Jun 12;9(3):1249-1277. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c180034. Compr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31187891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of macrophage ion channels in the progression of atherosclerosis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 31;14:1225178. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1225178. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37588590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic TRPC3 loss contributes to chronic alcohol consumption-induced hepatic steatosis and liver injury in mice.Life Metab. 2023 Dec 18;3(1):load050. doi: 10.1093/lifemeta/load050. eCollection 2024 Feb. Life Metab. 2023. PMID: 39871879 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bondini S, Kleiner DE, Goodman ZD, Gramlich T, Younossi ZM. Pathologic assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin Liver Dis 11: 17–23, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

