Glutamate and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Systems in the Pathophysiology of Major Depression and Antidepressant Response to Ketamine
- PMID: 27449797
- PMCID: PMC5107161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.05.005
Glutamate and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Systems in the Pathophysiology of Major Depression and Antidepressant Response to Ketamine
Abstract
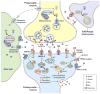
In patients with major depressive disorder or bipolar disorder, abnormalities in excitatory and/or inhibitory neurotransmission and neuronal plasticity may lead to aberrant functional connectivity patterns within large brain networks. Network dysfunction in association with altered brain levels of glutamate and gamma-aminobutyric acid have been identified in both animal and human studies of depression. In addition, evidence of an antidepressant response to subanesthetic-dose ketamine has led to a collection of studies that have examined neurochemical (e.g., glutamatergic and gamma-aminobutyric acidergic) and functional imaging correlates associated with such an effect. Results from these studies suggest that an antidepressant response in association with ketamine occurs, in part, by reversing these neurochemical/physiological disturbances. Future studies in depression will require a combination of neuroimaging approaches from which more biologically homogeneous subgroups can be identified, particularly with respect to treatment response biomarkers of glutamatergic modulation.
Keywords: Bipolar disorder; Glutamate; Ketamine; Major depressive disorder; Mood disorder; NMDA receptor antagonist.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Trullas R, Skolnick P. Functional antagonists at the NMDA receptor complex exhibit antidepressant actions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990;185:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Maeng S, Zarate CA, Jr, Du J, Schloesser RJ, McCammon J, Chen G, et al. Cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine: role of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;63:349–352. - PubMed
-
- Musazzi L, Racagni G, Popoli M. Stress, glucocorticoids and glutamate release: effects of antidepressant drugs. Neurochem Int. 2011;59:138–149. - PubMed
-
- Skolnick P, Layer RT, Popik P, Nowak G, Paul IA, Trullas R. Adaptation of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors following antidepressant treatment: implications for the pharmacotherapy of depression. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1996;29:23–26. - PubMed
-
- Nowak G, Trullas R, Layer RT, Skolnick P, Paul IA. Adaptive changes in the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex after chronic treatment with imipramine and 1-aminocyclopropanecarboxylic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:1380–1386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

