TGF-β Signaling from Receptors to Smads
- PMID: 27449815
- PMCID: PMC5008074
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022061
TGF-β Signaling from Receptors to Smads
Abstract
Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and related growth factors are secreted pleiotropic factors that play critical roles in embryogenesis and adult tissue homeostasis by regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, death, and migration. The TGF-β family members signal via heteromeric complexes of type I and type II receptors, which activate members of the Smad family of signal transducers. The main attribute of the TGF-β signaling pathway is context-dependence. Depending on the concentration and type of ligand, target tissue, and developmental stage, TGF-β family members transmit distinct signals. Deregulation of TGF-β signaling contributes to developmental defects and human diseases. More than a decade of studies have revealed the framework by which TGF-βs encode a context-dependent signal, which includes various positive and negative modifiers of the principal elements of the signaling pathway, the receptors, and the Smad proteins. In this review, we first introduce some basic components of the TGF-β signaling pathways and their actions, and then discuss posttranslational modifications and modulatory partners that modify the outcome of the signaling and contribute to its context-dependence, including small noncoding RNAs.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

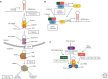
References
-
- Abdollah S, Macias-Silva M, Tsukazaki T, Hayashi H, Attisano L, Wrana JL. 1997. TβRI phosphorylation of Smad2 on Ser465 and Ser467 is required for Smad2–Smad4 complex formation and signaling. J Biol Chem 272: 27678–27685. - PubMed
-
- Agricola E, Randall RA, Gaarenstroom T, Dupont S, Hill CS. 2011. Recruitment of TIF1γ to chromatin via its PHD finger-bromodomain activates its ubiquitin ligase and transcriptional repressor activities. Mol Cell 43: 85–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
