Cellular conservation of endangered midget buffalo (Lowland Anoa, Bubalus quarlesi) by establishment of primary cultured cell, and its immortalization with expression of cell cycle regulators
- PMID: 27449922
- PMCID: PMC5023572
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-016-0004-0
Cellular conservation of endangered midget buffalo (Lowland Anoa, Bubalus quarlesi) by establishment of primary cultured cell, and its immortalization with expression of cell cycle regulators
Abstract
Lowland Anoa has become endangered due to hunting and human activity. Protection and breeding of endangered species in a controlled environment is the best way of conservation. However, it is not possible to adopt this approach for all endangered species because of the cost involved and the ever-increasing number of critically endangered species. In consideration of these limitations to the conventional conservation methods, we established a primary cell culture of endangered buffalo (Lowland Anoa, Bubalus quarlesi), for the preservation of this biological resource. In addition, we introduced human derived, mutant cyclin dependent kinase 4 (CDK4), Cyclin D, and telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) into the primary cells. The successful introduction of these three genes was confirmed by western blot with specific antibodies, and enzymatic activity. We also showed that the expression of mutant CDK4, Cyclin D, and TERT allows us to efficiently establish an immortalized cell line, with an intact chromosome pattern, from Lowland Anoa. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first investigation that established an immortalized cell line of an endangered wild animal species.
Keywords: Cellular conservation; Cultured cells; Endangered animals; Immortalization.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest to disclose for this manuscript
Figures


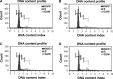
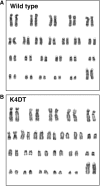


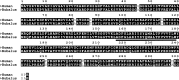
References
-
- Associated-Press (2009) San Diego’s Frozen Zoo. http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2002/10/14/tech/main525521.shtml
-
- Burton JA, Hedges S, Burton JA. The taxonomic status, distribution and conservation of the lowland anoa Bubalus depressicornis and mountain anoa Bubalus quarlesi. Mammal Rev. 2005;35:25–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2907.2005.00048.x. - DOI
-
- Donai K, Kiyono T, Eitsuka T, Guo Y, Kuroda K, Sone H, Isogai E, Fukuda T T. Bovine and porcine fibroblasts can be immortalized with intact karyotype by the expression of mutant cyclin dependent kinase 4, cyclin D, and telomerase. J Biotechnol. 2014;176:50–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2014.02.017. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

