Leigh-Like Syndrome Due to Homoplasmic m.8993T>G Variant with Hypocitrullinemia and Unusual Biochemical Features Suggestive of Multiple Carboxylase Deficiency (MCD)
- PMID: 27450367
- PMCID: PMC5413447
- DOI: 10.1007/8904_2016_559
Leigh-Like Syndrome Due to Homoplasmic m.8993T>G Variant with Hypocitrullinemia and Unusual Biochemical Features Suggestive of Multiple Carboxylase Deficiency (MCD)
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Leigh-Like Syndrome Due to Homoplasmic m.8993T>G Variant with Hypocitrullinemia and Unusual Biochemical Features Suggestive of Multiple Carboxylase Deficiency (MCD).JIMD Rep. 2017;33:111. doi: 10.1007/8904_2017_588. JIMD Rep. 2017. PMID: 29076057 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
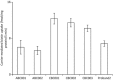
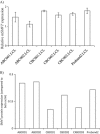
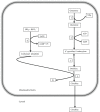
Leigh syndrome (LS), or subacute necrotizing encephalomyelopathy, is a genetically heterogeneous, relentlessly progressive, devastating neurodegenerative disorder that usually presents in infancy or early childhood. A diagnosis of Leigh-like syndrome may be considered in individuals who do not fulfil the stringent diagnostic criteria but have features resembling Leigh syndrome.We describe a unique presentation of Leigh-like syndrome in a 3-year-old boy with elevated 3-hydroxyisovalerylcarnitine (C5-OH) on newborn screening (NBS). Subsequent persistent plasma elevations of C5-OH and propionylcarnitine (C3) as well as fluctuating urinary markers were suggestive of multiple carboxylase deficiency (MCD). Normal enzymology and mutational analysis of genes encoding holocarboxylase synthetase (HLCS) and biotinidase (BTD) excluded MCD. Biotin uptake studies were normal excluding biotin transporter deficiency. His clinical features at 13 months of age comprised psychomotor delay, central hypotonia, myopathy, failure to thrive, hypocitrullinemia, recurrent episodes of decompensation with metabolic keto-lactic acidosis and an episode of hyperammonemia. Biotin treatment from 13 months of age was associated with increased patient activity, alertness, and attainment of new developmental milestones, despite lack of biochemical improvements. Whole exome sequencing (WES) analysis failed to identify any other variants which could likely contribute to the observed phenotype, apart from the homoplasmic (100%) m.8993T>G variant initially detected by mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) sequencing.Hypocitrullinemia has been reported in patients with the m.8993T>G variant and other mitochondrial disorders. However, persistent plasma elevations of C3 and C5-OH have previously only been reported in one other patient with this homoplasmic mutation. We suggest considering the m.8993T>G variant early in the diagnostic evaluation of MCD-like biochemical disturbances, particularly when associated with hypocitrullinemia on NBS and subsequent confirmatory tests. An oral biotin trial is also warranted.
Keywords: Acylcarnitines; Citrulline; Leigh syndrome; Newborn screening (NBS); mtDNA mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baumgartner MR, Hu CA, Almashanu S, et al. Hyperammonemia with reduced ornithine, citrulline, arginine and proline: a new inborn error caused by a mutation in the gene encoding delta (1)-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase. Hum Mol Genet. 2000;9(19):2853–2858. doi: 10.1093/hmg/9.19.2853. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bindoff L. Mitochondrial gastroenterology. In: DiMauro S, Hirano M, Schon EA, editors. Mitochondrial medicine. Abingdon: Informa Healthcare; 2006. pp. 143–159.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

