Differences in Cognitive Function of Rats with Traumatic Brain Injuries Following Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
- PMID: 27450528
- PMCID: PMC4968614
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.899548
Differences in Cognitive Function of Rats with Traumatic Brain Injuries Following Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy
Abstract
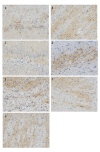
BACKGROUND Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) is a historical therapeutic option in the treatment of various types of brain damage. At present, clinical treatment of hypoxic-ischemic injury is giving priority to cognitive training. The effects of HBO on cognitive dysfunction were observed in a controlled cortical impact (CCI) rat model. MATERIAL AND METHODS Seventy male SD rats were randomly divided into control (n=10) and intervention (n=60) groups. All rats underwent baseline water maze testing 1 day before modeling, and were retested 8 weeks after modeling. The percentage of residence time during escape latency in the target quadrant and the total time were recorded. Data were analyzed by SPSS 16.0 software. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS After 8 weeks, no statistical difference (P>0.05) existed in spatial learning ability in the 3-day and 5-day groups when compared with baseline. The other groups were statistically different by auto-comparison (P<0.05). No statistical difference (P>0.05) in spatial memory existed in the 5-day and 1-week groups when compared with baseline, while a significant difference was noted in the other groups by self-comparison (P<0.05). No statistical difference (P>0.05) was noted in the level of expression of growth-associated protein-43 (GAP-43) and synaptophysin (Syn) in the 1-day group compared with the control group. The remaining groups and the control group were statistically different (P<0.05), while the level of expression of GAP-43 and Syn in the 5-day, 1-week, and 2-week groups was significantly different compared with that in the control group (P<0.01). CONCLUSIONS If HBO therapy was provided 5-7 days after craniocerebral trauma, there was apparent improvement in cognitive function and neuroplasticity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of hyperbaric oxygen on synaptic ultrastructure and synaptophysin expression in hippocampus of neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Mar;48(3):199-203. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 20426956 Chinese.
-
[Long-term effects of early hyperbaric oxygen therapy on neonatal rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Jun;8(3):216-20. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16787595 Chinese.
-
Hyperbaric oxygenation promotes neural stem cell proliferation and protects the learning and memory ability in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Feb 1;8(2):1752-9. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25973064 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of combined therapy with ephedrine and hyperbaric oxygen on neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury.Neurosci Lett. 2009 Nov 13;465(2):171-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.09.011. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Neurosci Lett. 2009. PMID: 19765636
-
[Optimal therapeutic window of hyperbaric oxygenation in neonatal rat with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Mar;44(3):177-81. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16624051 Chinese.
Cited by
-
A review on the neuroprotective effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy.Med Gas Res. 2021 Apr-Jun;11(2):72-82. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.311498. Med Gas Res. 2021. PMID: 33818447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy reduces astrogliosis and helps to recovery brain damage in hydrocephalic young rats.Childs Nerv Syst. 2018 Jun;34(6):1125-1134. doi: 10.1007/s00381-018-3803-0. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Childs Nerv Syst. 2018. PMID: 29671042
References
-
- Chen LF, Tian YF, Lin CH, et al. Repetitive hyperbaric oxygen therapy provides better effects on brain inflammation and oxidative damage in rats with focal cerebral ischemia. J Formos Med Assoc. 2014;113:620–28. - PubMed
-
- Duan S, Shao G, Yu L, Ren C. Angiogenesis contributes to the neuroprotection induced by hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Int J Neurosci. 2015;125:625–34. - PubMed
-
- Xue F, Huang JW, Ding PY, et al. Nrf2/antioxidant defense pathway is involved in the neuroprotective effects of Sirt1 against focal cerebral ischemia in rats after hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning. Behav Brain Res. 2016;309:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Dixon CE, Lyeth BG, Povlishock JT, et al. A fluid percussion model of experimental brain injury in the rat. J Neurosurg. 1987;67(1):110–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

