ASCT2 (SLC1A5) is an EGFR-associated protein that can be co-targeted by cetuximab to sensitize cancer cells to ROS-induced apoptosis
- PMID: 27450723
- PMCID: PMC5017913
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.07.020
ASCT2 (SLC1A5) is an EGFR-associated protein that can be co-targeted by cetuximab to sensitize cancer cells to ROS-induced apoptosis
Abstract
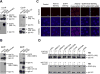
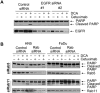
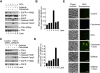
Therapeutic targeting of ASCT2, a glutamine transporter that plays a major role in glutamine uptake in cancer cells, is challenging because ASCT2 also has a biological role in normal tissues. In this study, we report our novel finding that ASCT2 is physically associated in a molecular complex with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is often overexpressed in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Furthermore, we found that ASCT2 can be co-targeted by cetuximab, an EGFR antibody approved for treating metastatic HNSCC. We demonstrated that cetuximab downregulated ASCT2 in an EGFR expression-dependent manner via cetuximab-mediated EGFR endocytosis. Downregulation of ASCT2 by cetuximab led to decreased intracellular uptake of glutamine and subsequently a decreased glutathione level. Cetuximab thereby sensitized HNSCC cells to reactive oxygen species (ROS)-induced apoptosis and, importantly, it is independent of effective inhibition of EGFR downstream signaling by cetuximab. In contrast, knockdown of EGFR by siRNA or inhibition of EGFR kinase with gefitinib, an EGFR kinase inhibitor, failed to sensitize HNSCC cells to ROS-induced apoptosis. Our findings support a novel therapeutic strategy for EGFR-overexpressing and cetuximab-resistant cancers by combining cetuximab with an oxidative therapy.
Keywords: ASCT2; Cetuximab; EGFR; Glutathione; HNSCC; ROS.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests in relation to the work described.
Figures
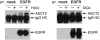

Similar articles
-
AP1G1 is involved in cetuximab-mediated downregulation of ASCT2-EGFR complex and sensitization of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to ROS-induced apoptosis.Cancer Lett. 2017 Nov 1;408:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28823958 Free PMC article.
-
ASCT2 (SLC1A5)-dependent glutamine uptake is involved in the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2020 Jan;122(1):82-93. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0637-9. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Br J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31819178 Free PMC article.
-
Rational combination with PDK1 inhibition overcomes cetuximab resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.JCI Insight. 2019 Oct 3;4(19):e131106. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.131106. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 31578313 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular targeted therapies in the management of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: recent developments and perspectives.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Mar;13(3):389-402. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23092267 Review.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Inhibition in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck.Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2015 Dec;29(6):1011-32. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2015.07.007. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 26568545 Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of circular RNA septin 9 inhibits the malignant progression of breast cancer by reducing the expression of solute carrier family 1 member 5 in a microRNA-149-5p-dependent manner.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):10624-10637. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2000731. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34738502 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting of glutamine transporter ASCT2 and glutamine synthetase suppresses gastric cancer cell growth.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 May;144(5):821-833. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2605-9. Epub 2018 Feb 12. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29435734 Free PMC article.
-
AP1G1 is involved in cetuximab-mediated downregulation of ASCT2-EGFR complex and sensitization of human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells to ROS-induced apoptosis.Cancer Lett. 2017 Nov 1;408:33-42. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28823958 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking EREG/GPX4 Sensitizes Head and Neck Cancer to Cetuximab through Ferroptosis Induction.Cells. 2023 Feb 24;12(5):733. doi: 10.3390/cells12050733. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36899869 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between amino acid metabolism and self-renewal of cancer stem cells: Perspectives in cancer therapy.World J Stem Cells. 2022 Apr 26;14(4):267-286. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v14.i4.267. World J Stem Cells. 2022. PMID: 35662861 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kanai Y, Hediger MA. The glutamate/neutral amino acid transporter family SLC1: molecular, physiological and pharmacological aspects. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:469–479. - PubMed
-
- McGivan JD, Bungard CI. The transport of glutamine into mammalian cells. Front Biosci. 2007;12:874–882. - PubMed
-
- Dang CV. Glutaminolysis: supplying carbon or nitrogen or both for cancer cells? Cell Cycle. 2010;9:3884–3886. - PubMed
-
- Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:579–591. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

